Recent features
HS2 Cuts: A Second Chance for Liverpool
As we wave goodbye to any ideas of HS2 reaching the north, a deafening chorus of betrayal is drowning out attempts to assess the project’s worth more rationally. Yet the inconvenient truth is that many in the north have never been convinced of the value of HS2. In this article, Martin Sloman, a director at influential lobby group, 20 Miles More, asks whether the HS2 re-set is a golden opportunity for Liverpool - a second chance at creating new transport infrastructure that works for our city?
Martin Sloman
As we wave goodbye (at least for now) to any ideas of HS2 reaching the north, a deafening chorus of betrayal is drowning out attempts to assess the project’s worth more rationally. Yet for all that, there is an inconvenient truth displayed every time a BBC journalist puts a microphone in front of the general public - the existence of a clear disconnect between the project’s advocates and your average paying train passenger. Lord Adonis may cry foul but many in the north have never been convinced of the value of HS2. In this article, Martin Sloman, a director at influential lobby group, 20 Miles More, considers the matter from Liverpool’s perspective. He asks the question, is the HS2 re-set a golden opportunity - a second chance at creating new transport infrastructure that works for our city?
And so there it is. HS2 beyond Birmingham has gone the way of the Dodo. It is no more. It has ceased to be. It is an ex-railway.
Prime Minister, Rishi Sunak’s much trailed announcement at the Conservative Party Conference to hack back the UK’s largest public transport project represents not just a big throw of the political dice, but a huge scaling back of HS2’s ambitions. Unless you believe a Starmer-led Labour government will revive the scheme (don’t bank on it), the line will no longer extend to Manchester, instead terminating at Birmingham, the place that likes to call itself ‘the second city’. Brum’s claims have been bolstered now. This news is seen almost universally amongst the commentariat as a body blow to the much-vaunted ‘Levelling Up’ strategy, but what does it mean for Liverpool and our city region? Should we see it less as a disaster for the north and more as a second chance to get our city’s transport infrastructure right?
Liverpool came late to the HS2 debate. It was only after the Phase 2 proposal was revealed in January 2013 that we began to realise how the project would affect us. By then, the route was set in stone, and it didn’t look good. The new line was designed as if Liverpool didn’t exist. There would be stations at Manchester Piccadilly and Manchester Airport, a lengthy tunnel into Manchester city centre and a link to the north via Wigan. Liverpool would be lucky to get new, plastic platform seating.
Under the HS2 plan, its high speed trains would run from Liverpool to London but would first need to traverse almost 40 miles of Victorian railways at slower speeds before accessing new, gleaming track south of Crewe. The Liverpool service would be limited to the shorter 200m ‘classic compatible’ trains with half the seats and would run two services per hour with a running time to London of one hour and 34 minutes. Meanwhile, Manchester would receive the gold-plated service - three 400m double-length ‘captive’ trains per hour, speeding to the capital in one hour and 8 minutes – three times Liverpool’s capacity and 28% faster – the end of historic parity in connections to the south.
The lack of high-speed infrastructure to serve Liverpool would prevent the release of capacity on our existing local network, which was supposed to be one of the selling points of HS2. This would severely limit the development of new passenger and freight services and ran contrary to the recommendations of ‘Rebalancing Britain: Policy or Slogan?’ – the Heseltine / Leahy report of 2011 which stated:
‘Government should amend the currently proposed High Speed 2 route, so it connects to both Manchester and Liverpool directly. In the same time frame and to the same standard, Government should commit to assuring Liverpool’s historic parity with Manchester for travel time to London and thereby avoid harmful competitive disadvantage to Liverpool in attracting inward investment’.
That harmful competitive disadvantage was confirmed by accounting giants KPMG who produced their report – HS2 Regional Economic Impacts on behalf of HS2 in 2013. It showed maps of Britain covered in big green circles, where HS2 would uplift the economy of cities and towns. There were, however, little red circles and they were less good news and one of them was over Liverpool. To be fair, the report claimed Liverpool’s GDP could be uplifted by 1.2% in ‘favourable’ conditions, but equally it could shrink by 0.5% in ‘unfavourable’ ones. Not exactly a ringing endorsement and a worse outcome than for towns and cities that were not even connected to the network in any way, such as Hull.
In response to this threat, a coalition of academics and local business figures led by Andrew Morris banded together to form 20 Miles More, an independent campaign group lobbying for a direct, dedicated link to HS2. The 20 miles referenced in the name referred to the length of the shortest link to the HS2 network. Our group, of which I was a director, produced reports, met with political, business and transport leaders and responded to consultations. The assistance of political consultants Jon Egan and Phillip Blond helped us to secure television coverage for our launch event.
Something must have stirred because not long after the Liverpool City Region Combined Authority and the local councils woke up to the danger and launched their own campaign called Linking Liverpool and we’d like to think we had something to do with that. They calculated that a direct Liverpool link to HS2 would be worth £15 billion to the local economy and secure 20,000 new jobs. At last, the issue facing our city was being taken seriously.
“That harmful competitive disadvantage was confirmed by accounting giants KPMG. Their report showed maps of Britain covered in big green circles, where HS2 would uplift the economy of cities and towns. There were, however, little red circles and they were less good news and one of them was over Liverpool.”
One point that we made in our report was that a Liverpool link to HS2 could form part of a new rail link to Manchester and over the Pennines to Leeds. We felt vindicated when the Northern Powerhouse Rail initiative was launched in 2014. This envisaged six northern cities – Liverpool, Manchester, Leeds, Hull, Sheffield and Newcastle being linked by new high speed rail infrastructure. This resonated with Boris Johnson’s ‘Levelling up’ agenda.
In 2020, construction work on the first phase of HS2 (London to Birmingham) started and the realities began to strike home. The prospect of miles of countryside being torn up for a new railway generated local opposition and the wrath of environmental groups, especially in the home counties, but it was the rapidly escalating cost of the project that really concentrated minds. An initial 2010 estimate of £33 billion had now ballooned to £71 billion with some commentators suggesting the final figure could be well over £100 billion.
Why costs spiralled out of control may be down to a number of reasons – overspecification of the initial project, inflation, procurement issues, planning delays, environmental mitigation, and of course, government interference. The result was cutbacks and delays, culminating in Rishi Sunak’s announcement at the Tory’s Manchester Conference – bad news for ‘the north’ delivered in the self-declared heart of ‘the north’, eyeball to eyeball.
Figure 1
Routes and phasing of HS2 as they stand following Sunak’s recent announcement.
Looking at the map, what Sunak has done is to prune HS2 back to Phase 1, which runs from London to Birmingham. Gone is Phase 2a from Birmingham to Crewe, Phase 2b (East) from Birmingham to East Midlands Parkway and Phase 2b (West) from Crewe to Manchester. What has been retained is the link from London Euston to Old Oak Common (reportedly now subject to finding private sector investment) – vital for delivering an effective HS2 service – as well as the link at Lichfield (Handsacre) junction to the existing West Coast Main Line, which allows trains from Liverpool and Manchester to make use of HS2.
The implications for the North West are significant and on the upside, the damaging inequality between Liverpool and Manchester identified by Heseltine and Leahy has been removed. So, from the completion of Phase One (currently scheduled for some time between 2029 and 2033), both Liverpool and Manchester will have services to London making use of existing tracks as far as Lichfield. Trains will run on HS2 for over 60% of the distance from London to the North West with the remainder of the journey on the much slower classic network. That will give a journey time to Liverpool of around one hour and 46 minutes and to Manchester of one hour and 41 minutes. This five-minute difference contrasts with the 26-minute difference that would have occurred had Phase 2b gone ahead. Liverpool’s train capacity will be unaffected, remaining at two 200m long units per hour (each carrying up to 550 passengers) - whereas Manchester will see a halving of its promised capacity to three 200m units. This is because the 400m long, 1100 passenger ‘captive’ trains (trains that can only run on the new HS2 route) that were to serve Manchester under the original plans can no longer do so.
“It is difficult to support a proposal that would deliver so little to our city and so much to a city that is an economic rival.”
The reduction in overall train capacity and increase in journey time is, of course, a body blow to the North West and has resulted in accusations of betrayal in certain quarters. But while the avoidance of baked-in disadvantage between our two cities might provoke a sigh of relief in some, it would be wrong to assume that what is bad for Manchester must be good for Liverpool. As Jon Egan pointed out in his recent Liverpolitan article, Mancpool: One Mayor, One Authority, One Vision, the real disparity is not so much between Liverpool and Manchester but between the two cities and London. However, it is difficult to support a proposal that would deliver so little to our city and so much to a city that is an economic rival.
Rethinking Northern Powerhouse Rail
Another victim of the latest cuts is Northern Powerhouse Rail. This body is to be replaced by a new entity known as Network North and improved journey times are promised from Manchester to Bradford, Sheffield and Hull with £12 billion allocated to a link between Manchester and Liverpool. How that money is to be spent will be the subject of agreement between our civic leaders (and presumably other North West towns such as Warrington).
Northern Powerhouse Rail envisaged high speed lines linking the main cities of the North West. However, when the Department of Transport published the Integrated Rail Plan (IRP) in 2021, these aspirations were somewhat diluted.
Figure 2:
The Integrated Rail Plan (2021) - not so integrated now
“What does all this mean for that ring-fenced £12bn route between Liverpool and Manchester? Will there still be a requirement for the Manchester Airport tunnel? Budgeted around the £5bn mark (before inflation hit) that would take a hefty chunk out of the available cash.”
According to the IRP plan, the Liverpool to Manchester rail route would be achieved by a mixture of upgraded freight and passenger lines, some new construction and the Manchester branch of HS2.
This arrangement was never optimum – being seen as a ‘bolt-on extra’ to HS2. However, it did directly connect Liverpool to the new rail network allowing a London connection to HS2 via Tatton Junction.
Changes were made to the IRP routing following the publication of Sir Peter Hendy’s Union Connectivity Review in November 2021. Hendy identified that the best way of increasing passenger and freight capacity to Scotland and Northern Ireland (via the Port of Liverpool) was by upgrading the existing West Coast Main Line north of Crewe.
The proposed route of HS2 to the North – the ‘Golborne Spur’ to the east of Warrington - was subsequently deleted and a review put in place to determine an alternative route that better met the aspirations of the Hendy report. This is, for now, clearly off the agenda.
So, what does all this mean for that ring-fenced £12bn route between our cities? Will it stay the same or once again morph into something else? Certainly, this is an opportunity to completely rethink the Liverpool to Manchester link. For example, will there still be a requirement for the Manchester Airport tunnel? If so, budgeted around the £5bn mark (before inflation hit) that would take a hefty chunk out of the available cash – although it is difficult to see how else a new link can be run into central Manchester. However, given that there is no longer a need to accommodate HS2, strictly speaking there’s no reason why an improved alignment can’t be sought. But there may be other ways to spend the money.
A Mersey Crossrail?
Prime Minister Sunak has promised that the £36 billion ‘saved’ by the cancellation of HS2 Phase 2 will be re-invested in a plethora of new transport projects. Mention has been made of electrifying the North Wales main line, extending the Midland Metro, a host of road projects and finally giving Leeds its long-promised metro. Given that the cancellation means that we in Liverpool will now suffer from reduced journey time to the capital, let’s hope that a reasonable slice of that money comes to our city.
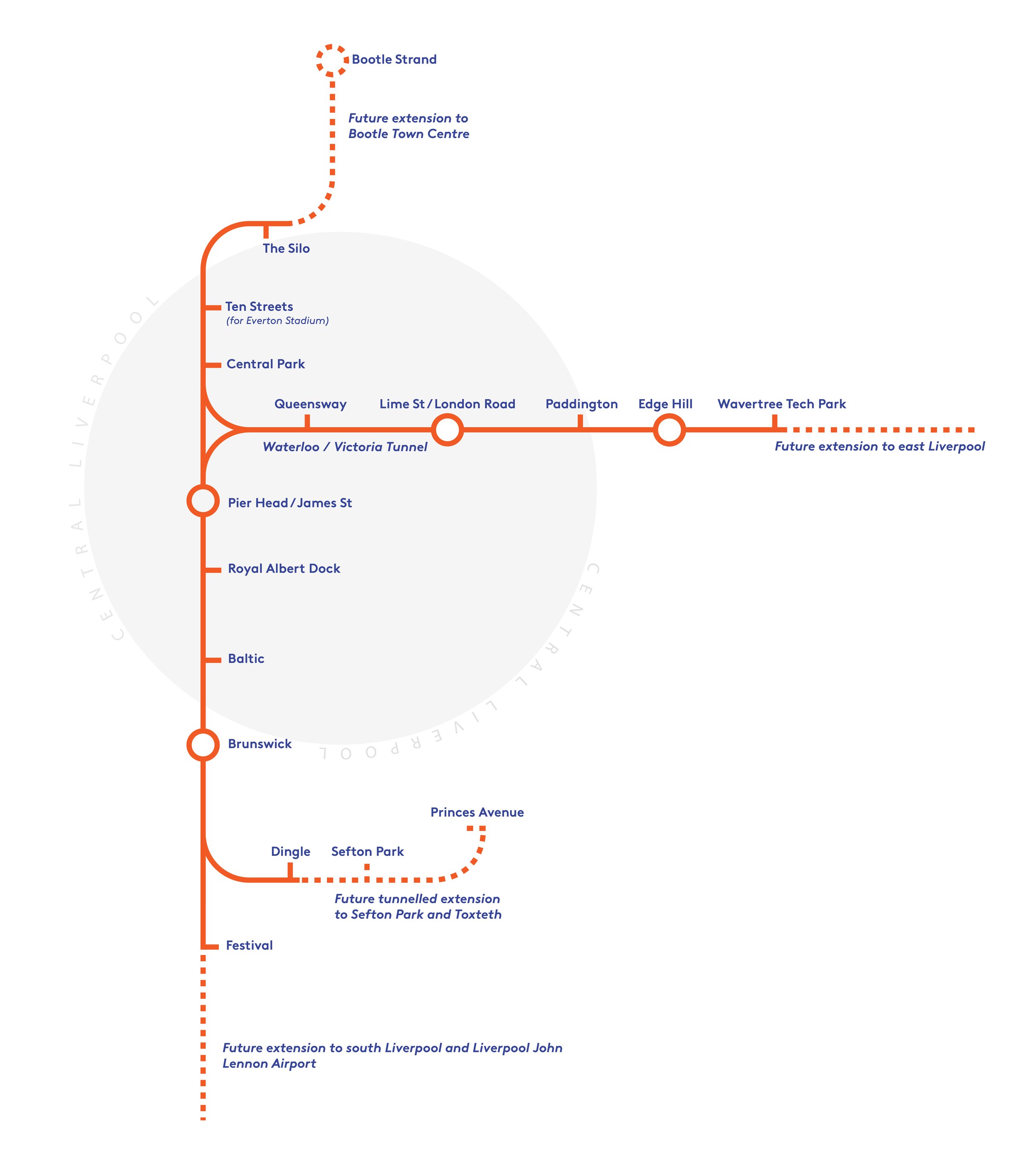
Liverpool has a developed transport network thanks to the infrastructure work of the 1970s, which gave us the Merseyrail system. However, one problem with the network is its limited coverage. The frequent electric trains running underground in the city centre only serve the Wirral, Sefton, a narrow strip of north, south and central Liverpool (but not the east) and a small part of Knowsley. That is a result of a failure to complete the original project following funding constraints in the mid-70s.
Now, we have the chance to complete that project – something that would give the Liverpool City Region a comprehensive rapid transit system second to none in the UK outside the capital.
I’m going to call it Mersey Crossrail because it would truly open up transit from north to south and east to west. It would make possible near seamless travel not only within Liverpool but also to the important network of satellite towns around and beyond the city region. The access to new job and lifestyle opportunities that would arise would be transformative for our people, while also encouraging modal shift to greener forms of transport. How much would this work cost? Probably in the region of £1 billion, which is a fraction of the cost of constructing a similar system in another city. That is because so much of the system is already in place.
So, what would this project entail? Apologies in advance because I’m now going to get into the nuts and bolts. I can’t help myself, I’m a rail enthusiast.
“Mersey Crossrail would make possible near seamless travel not only within Liverpool but also to the important network of satellite towns around and beyond the city region.”
Imagined, new Liverpool Central Station at the heart of an expanded Merseyrail network. Images by: mmcdstudio.
A 4-Step Transport Plan for Liverpool - Features and Benefits
Step 1. Expand Liverpool Central Station
First up, an expansion of Liverpool Central station, which currently hosts Northern Line services to Southport, Ormskirk, Kirkby and Hunts Cross. The station suffers from overcrowding due to its cramped island platform and the need for enlargement has long been recognised.. Widening the station envelope would not only improve the passenger experience, it would also unlock the next stage of transport expansion.
Step 2. Unlock the network by building the ‘Edge Hill Spur’
A new tunnel would be constructed from the south end of the station to Edge Hill connecting to the disused Wapping Tunnel which dates from the opening of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway in 1830. This proposal was formerly known as ‘The Edge Hill Spur’ and is the key to unlocking the true potential of the Merseyrail network because trains would now be able to run seamlessly east to west underneath the city streets in part by using old, mothballed underground tunnels. This Edge Hill link would effectively form a Mersey Crossrail with the prospect of services running between towns such as St Helens and West Kirby. Construction would involve minimal disruption to existing services thanks to header tunnels constructed back in the ‘70s.
The benefits of such a scheme are immense. Merseyrail would be cheaper to run because transiting through the city instead of terminating makes more economical use of trains and train crews, potentially increasing train frequency. However, it’s the expanded travel opportunities that would be the major plus.
Every station on Merseyrail would be within a maximum of one change of every other one. For example, City Line passengers would have direct access to Liverpool Central and Moorfields with their retail and employment opportunities or could run through to other destinations such as Birkenhead, Chester, Bootle or Southport.
“Every station on Merseyrail would be within a maximum of one change of every other one.”
Step 3. A new underground station for the Knowledge Quarter
One proposal that’s never made it off the drawing board is an underground station near to the university on Catherine Street serving the Hope / Myrtle Street area. Build the Mersey Crossrail and this could become a realistic option, not only adding important services for our legion of students and academics but also a much-needed shot in the arm for the broader Knowledge Quarter, including the strategically important Paddington Village area with its growing medical biotech cluster.
Step 4. Create new Merseyrail branches to the wider city region and beyond
With the partial reconstruction of a former flyover at Edge Hill, City Line services could link Runcorn to St Helens and Newton-le-Willows. This would add three more branches to the Merseyrail network covering a broader sweep of Liverpool, Knowsley, St Helens and Halton. Services could even be extended beyond the City Region boundary to Wigan, Manchester and Crewe thanks to the Northern Hub electrification schemes of the last decade and the introduction of the new fleet of Merseyrail trains with their dual voltage capability.
Another opportunity, which is already in progress, and which would benefit from additional funding, is the extension of the existing Merseyrail network using battery technology. We can now see this technology in operation with the opening of the new Kirkby Headbolt Lane station. This is served by trains running off the electrified network from the existing terminus at Kirkby. Future proposed destinations include Preston via Ormskirk, Warrington Bank Quay via Helsby, Wigan Walgate via Kirkby and, possibly the complete length of the ‘Borderlands’ Line from Bidston as far as Wrexham.
One great benefit of battery extensions, apart from avoiding the cost of extending electrification, is the opportunity to displace existing diesel services (e.g. Kirkby to Wigan, Ormskirk to Preston), so both reducing operating costs and harmful emissions.
Figure 3:
Shows the Merseyrail extensions possible with the Mersey Crossrail scheme. It also shows the existing proposals for battery extensions of the existing Wirral and Northern Lines.
With all of the proposed extensions in place, Merseyrail would become a powerful regional rail network, fully integrated into Liverpool City Centre. It would extend both into North East Wales and Greater Manchester.
It should be noted that, these extensions reflect the level of spending on transport expected for a city region the size of Liverpool, with a population of 1.5 million people. It is by no means extravagant.
The cancellation of Phase 2 of HS2 has been a blow for the North West region. However, the Liverpool City Region missed out on the initial proposals. Now, there is an excellent chance to redraw the rail map of the North West to give a more equitable distribution of the benefits that will still flow from the Phase 1 railway.
We now have a second chance with everything to play for. So, let’s hope that our political leaders take notice and deliver us the transport system that the region so clearly requires.
Martin Sloman is a civil engineer and former railway consultant. He is a director of the ‘20 Miles More’ lobby group, a coalition of academics and local business figures, which campaigned for a direct link from Liverpool to HS2.
What do you think? Let us know.
Add a comment below, join the debate via Twitter or Facebook or drop us a line at team@liverpolitan.co.uk
Ye Wha? Opera on the Mersey and other Mad Visions
For over ten years, 3D animator Michael McDonough, has been dreaming up new ways to re-imagine Liverpool’s urban landscape – designing outlandish opera houses, cathedral-like train stations, gothic bridges, and new visions for the docks. None of them have been built or are ever likely to be. But why does he bother? In this showcase of his work, Liverpolitan Editor, Paul Bryan explores Michael’s fascinating dreamscapes of the imagination.
Paul Bryan
“The way I come at things is to make no small plans. The city has had too much of that, too much dross, too much crap, too much small time thinking.”
So says Michael McDonough, Co-Founder here at Liverpolitan, and a man who has developed a bit of a reputation for his outspoken criticism of Liverpool’s (lack of) development scene. And in fairness, it’s a view that I, as the magazine’s Editor, often share.
One of the things that makes Michael interesting to me (other than the fact he’s had to develop skin as thick as a rhinosaurus to bat off ‘the army of gobshites’ who take him on or even pose as him online) is the fact that despite a successful career as a 3D designer and animator which has taken him to the capital, he continues through his design work to try to make a positive contribution to his home city of Liverpool and the discussion about its future. He does this without fanfare or gratitude and in fact, often in the face of quite complacent criticism from ‘locals’. Often by people with far less talent or insight than himself. For over ten years now, entirely under his own steam, Michael has been dreaming up new ways to re-imagine Liverpool’s urban landscape – designing outlandish opera houses, cathedral-like train stations, gothic bridges, and new visions for the docks. None of them have been built or are ever likely to be. They are not fully formed architectural plans, more dreamscapes of the imagination and we’ve made a showcase of that work in this feature article.
But why does he bother? What’s the point? Aren’t they just castles in the air built before AI and Midjourney made fantastical images the prerogative of all? To believe so would be to miss what’s really going on. There’s a much harder edge lying beneath the glossy visuals. He’s making the case for ambition as an antidote to a city-wide loss of nerve.
“We should be thinking in the same way world cities do like London, Singapore and New York. All these places have big ambitions. We should be looking to emulate that,” says McDonough. Instead, he believes Liverpool increasingly seems resigned to a lower status and too often its mediocre plans reflect that. Small schemes are favoured over transformative ones and then heralded as being the way forward. Anything substantial or showy is typically treated with hostility and suspicion.
“I keep hearing that in Liverpool we’re different, that we have our own models of success, but it’s a language of defeatism, masked and airbrushed as some kind of urban superiority.” He rejects this idea totally. “Being different doesn’t mean you reject ambition, scale and big ideas. That doesn’t make you different, it just makes you stupid.”
‘There’s an obsession in Liverpool’s planning circles with ‘context’ – the idea that new developments must be submissive to the city’s crown jewels."
Michael’s designs are meant in sharp contrast to the veritable cottage industry of ‘place-making’ peddlers, much favoured in recent years by our city leaders, whose low aspiration output chimes with this defeatist mindset. Meanwhile, the same old local architectural practices win job after job, churning out budget off-the-shelf buildings that further erode what makes the city special. There’s an obsession in Liverpool’s planning circles with ‘context’ – the idea that new developments must be submissive to the city’s crown jewels. But that attitude just results in bad buildings and Michael’s designs deliberately shun such restrictions. Some of his designs will inspire, but also enrage.
“The irony,” says McDonough, “is that those buildings we love so much are there purely because of ambition, because of power and commerce. They didn’t just land there as gifts from God.”
The point of history is to learn from it, not to fetishize it. We do Liverpool’s history a disservice by feeble attempts at mimicry. The Liverpool of yesteryear was bolder and more global in its perspective and if we are to take something useful from the past, it should be that. What Michael is attempting to do with these designs is to remind the city that it’s capable of bigger ideas, capable of re-imagining itself, capable of statement architecture, and capable of challenging its city rivals.
“What pushes me to create these designs is a desire to make people see the city differently – and by that I mean primarily the people who live and work within it. Because if we can awaken that boldness of old, so much is possible in our future,” says Michael. That is the lens through which he’d like people to view his designs. Of course, design is subjective. What might be considered beautiful by one person, can be viewed as horrendous by another but he claims to welcome those reactions. “One of our motivations for founding Liverpolitan magazine, was to create a place where thoughts and ideas on the city’s built environment could be shared, discussed and visualised – to think beyond self-constrained limitations,” he concludes. And indeed that is part of our mission.
So buckle in. This is Michael’s contribution. We hope others will be inspired to contribute in the future. It’s a long read. You may need a cup of tea. But there are lots of pretty pictures and food for thought.
Enjoy.
English National Opera, Liverpool
Post-Eurovision, Liverpool emerges with its reputation for hosting big events enhanced and attention inevitably turns to ‘what next?’ So how should the city attempt to capitalise on this positive exposure? Capitalise being the key word here – turning the benefits of a one-off event into something long-lasting, and preferably given a tangible physical form.
Step forward candidate 1: The English National Opera (ENO). This prestigious London-based institution has been told by its funders, Arts Council England, that if it wants the purse strings to remain untied, the institution needs to up-sticks and move to the regions, and rumour has it that Liverpool is very much on the short-list. Some will question why a city like Liverpool needs opera, but even if Tosca and Turandot are not your kind of thing, attracting such a high profile organisation will only add to Liverpool’s cultural offer and open up new job opportunities for young people who might otherwise fly the nest.
Dreaming up a new opera house on the banks of the Mersey, is something that dates back to the wild and unfunded dreams of former Mayor Joe Anderson. But this time, at least in theory, the prospect sounds a little more plausible. Not fully plausible mind – a recent article in The Post claimed the move might be more northern outpost than wholesale relocation, akin to Channel 4’s setup in Leeds. Still, it’s not completely out of the equation – especially if a new facility could combine uses with other functions – education, meeting space, performance arts. Back in 2021, the then-chancellor, Rishi Sunak allocated £2m for a feasibility study into some kind of new immersive music attraction. So despite initial talk of yet another Beatles-focused space, perhaps there’s scope for blending these projects onto one site to make the whole more achievable.
‘The point of history is to learn from it, not to fetishize it. We do Liverpool’s history a disservice by feeble attempts at mimicry.’
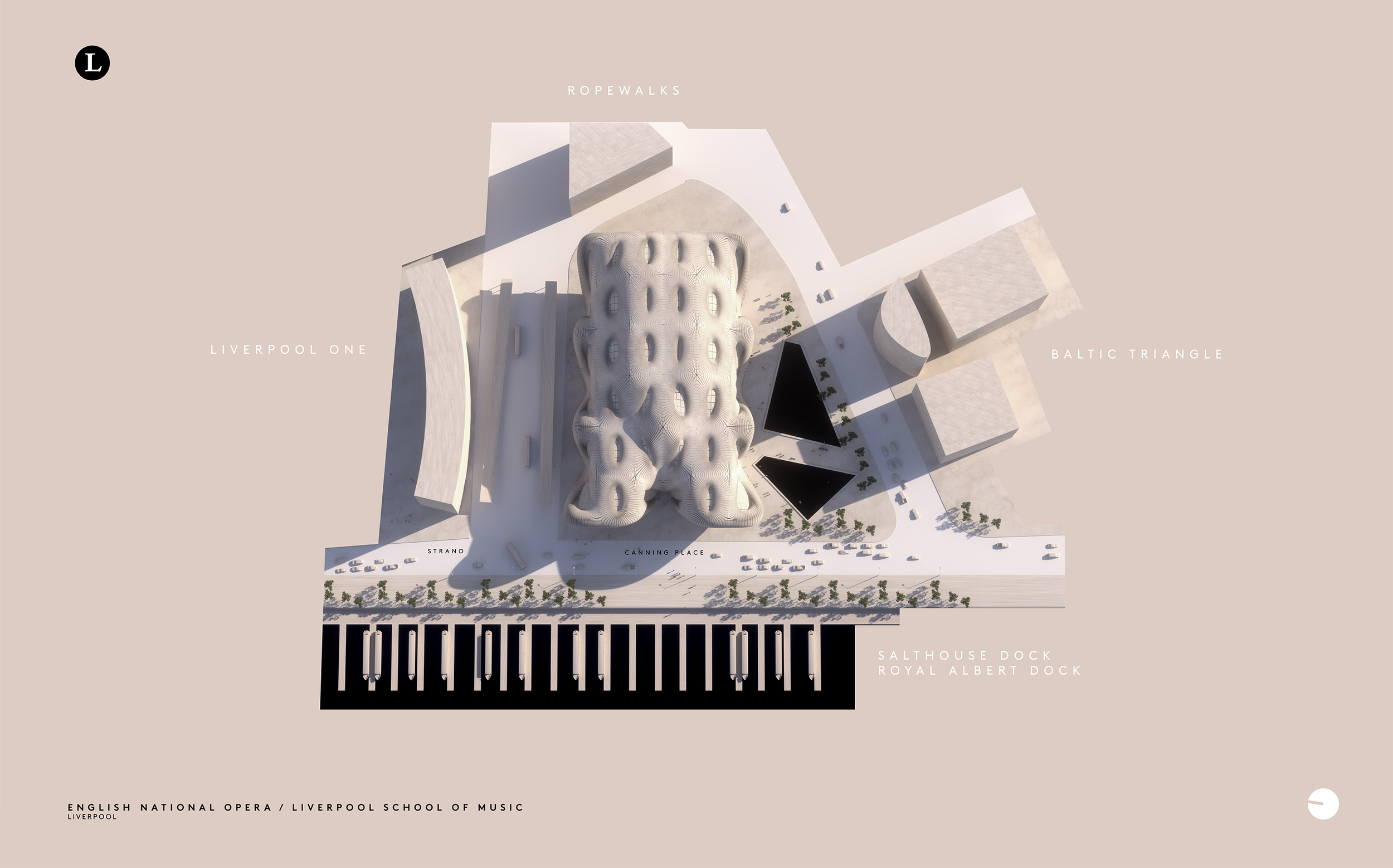
The most obvious location is the site of the now defunct former police station headquarters at Canning Place off the Strand. It’s a big site in a glamorous location with the potential to integrate the city centre more closely with the Baltic Triangle. In scale, Michael is proposing a building similar to the much lauded Copenhagen Opera House, which also has a waterfront setting, but he’s keen to avoid any slavish adherence to ‘context’ – “the space is big enough to create its own”, adding new aesthetic design cues to Liverpool’s urban environment rather than forever replicating (usually in impoverished form) what is already there. For Michael, this means “no warehouse-style blocks, no red-brick, and a departure from straight lines.” Some have said they can see a cobra snake in this design and others an elephant (hopefully not of the white variety). “I didn’t intend either but if they’re there, they’re there,” says Michael. “It’s all about organic, smooth, natural forms.” The final two images in the set, which show the interior of the main auditorium, were created using artificial intelligence more as an experiment in what is possible with the technology.
As an added bonus, Michael is proposing to demolish the John Lewis car park, which adds a “blocky barrier to the growth of the city centre eastwards,” as well as eroding the sense of occasion that this landmark structure deserves. A new solution would have to be found for the bus depot that sits beneath it (not to be confused with the Paradise Street Bus Station which would remain unaffected).





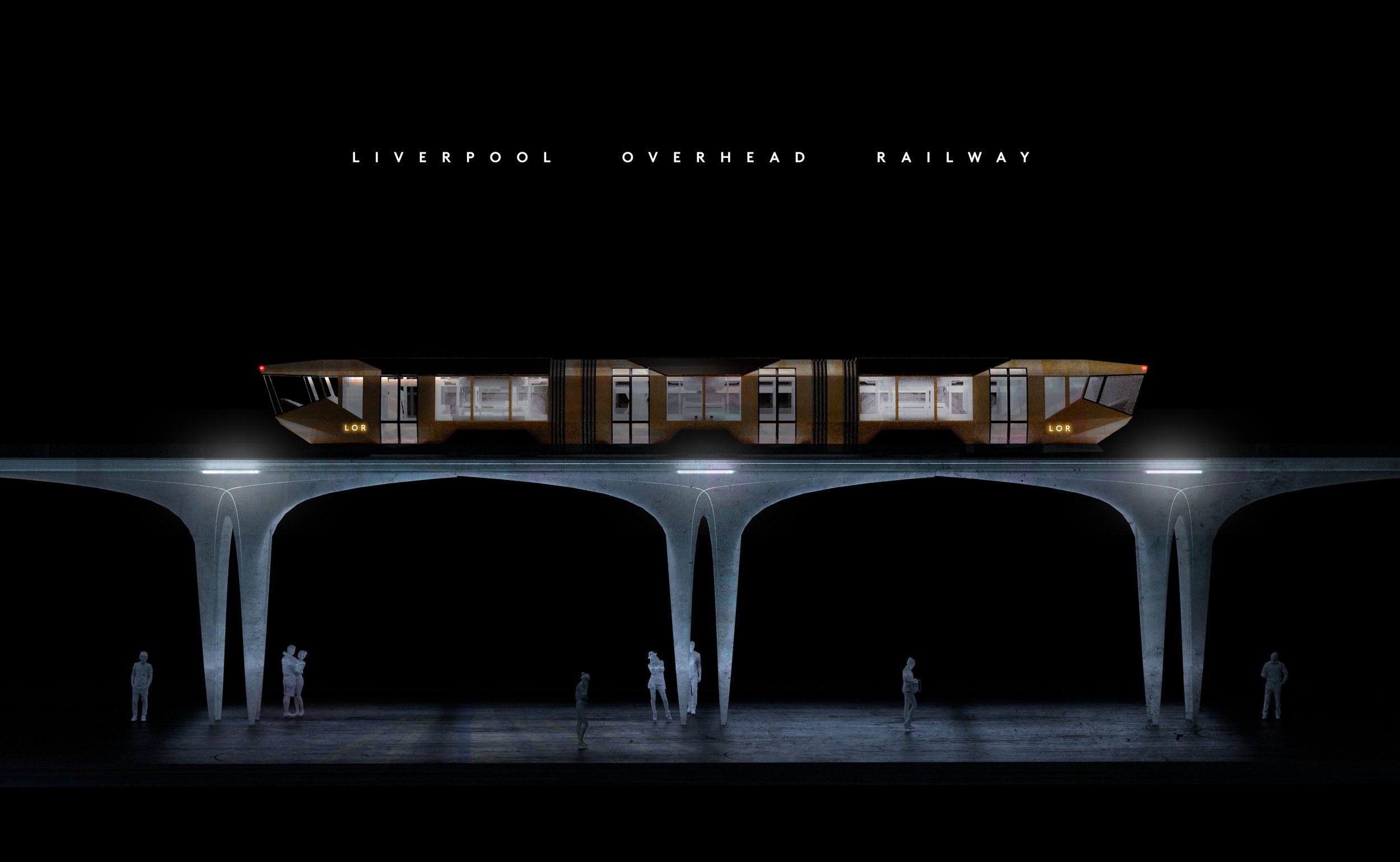
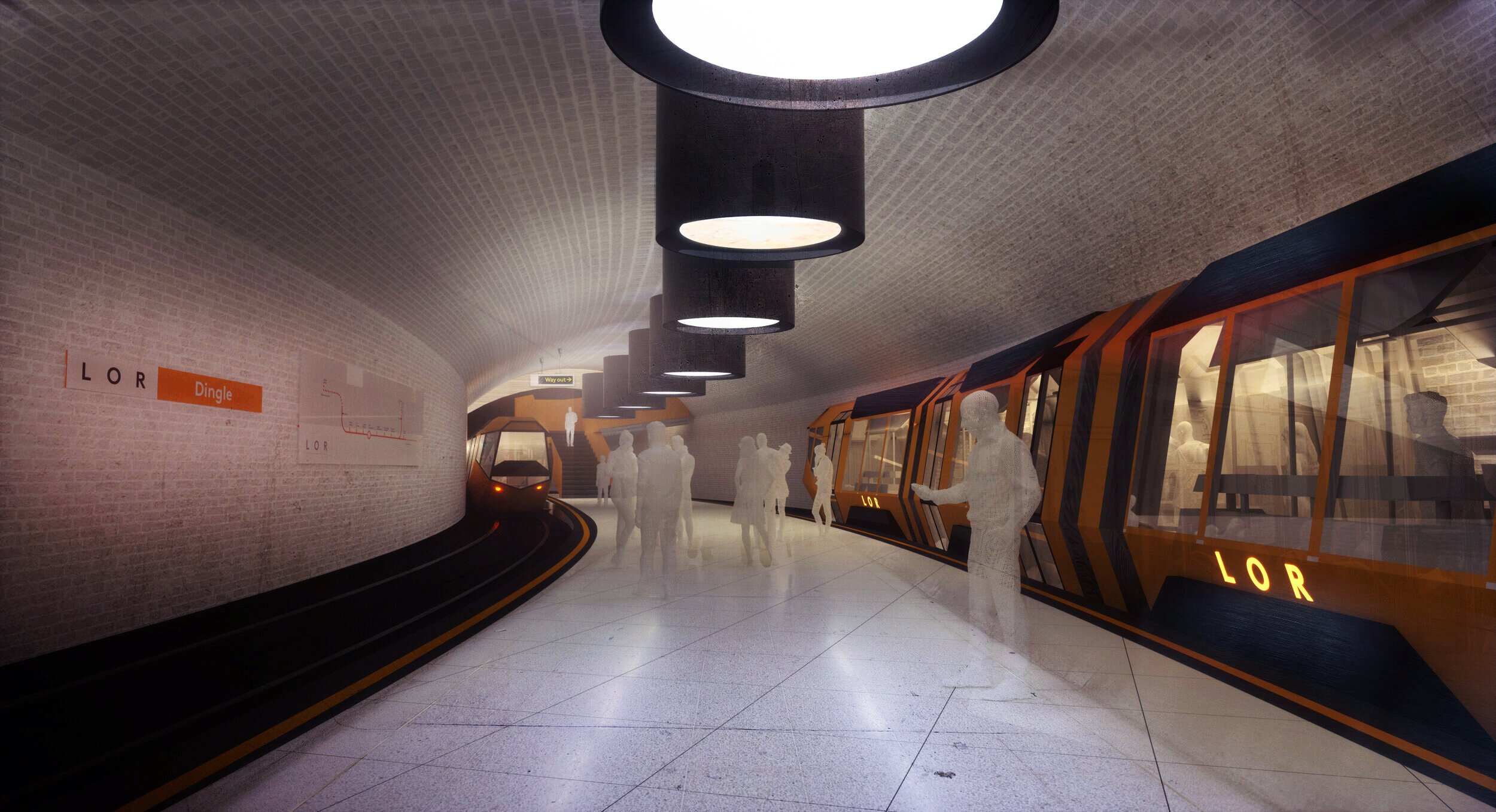
Liverpool Overhead Railway
Many people have long been fascinated by the Liverpool Overhead railway and perplexed by its loss. Extending seven miles along the length of the city’s impressive docklands from Seaforth and Litherland in the north to the Dingle in the south, the line survived for just 64 years before the decline in dock employment ate too deeply into its commuter base. There can be little doubt that if the Overhead Railway had survived into the modern era instead of being dismantled in 1956-57, it would have become another iconic symbol of Liverpool reminiscent of the Chicago ‘L’ trains. Not only that, but it may have long ago expedited the regeneration of the north docks into other uses. Instead, minus viable transport provision, we have had to watch on powerless as docks have lain derelict for decades under the tattered banner of Liverpool Waters.
As much as it’s fun to sit within an old Overhead carriage within the Liverpool Museum (and marvel at its spacious dimensions and varnished wooden interiors), Michael would much prefer to see it rebuilt. The case is becoming stronger with the soon to open Bramley Moore Dock Stadium, the Titanic Hotel and new apartments in the Tobacco warehouse extending the city centre and creating a line of activity to the attractions centred around the Albert Dock.
‘The Liverpool Overhead Railway may have long ago expedited the regeneration of the north docks into other uses. Instead, minus viable transport provision, we have had to watch on powerless as docks have lain derelict for decades under the tattered banner of Liverpool Waters.’
However, Michael says “we cannot and should not merely recreate a pastiche of the old line.” Technology and engineering have moved on, and the old structure was difficult and expensive to maintain. Besides, its heavy-set viaducts blocked views of the river from further inland, which might be unwelcome today. If the city are ever to rebuild the Liverpool Overhead Railway, he feels it should “celebrate the past but not be beholden to it.” A little like London’s Docklands Light Railway (DLR), his version 2.0 is a fully-fledged railway, not a monorail, elevated by organic and elegant concrete columns that avoid the blocky and very nineties form of the DLR design.
To maximise its utility, Michael’s new Liverpool Overhead Railway would not simply follow the old route but would connect more widely. Starting at Bootle in the north to better integrate that area as part of our metropolis, the line would connect the Everton stadium and key attractions centred around the Albert Dock before heading off south to the airport, and perhaps also east via the disused Waterloo or Victoria tunnels. The design of the structure would be modern, and the trains capable of running on conventional tracks (like the recently introduced Merseyrail ones) opening up options for integration with the wider rail network.
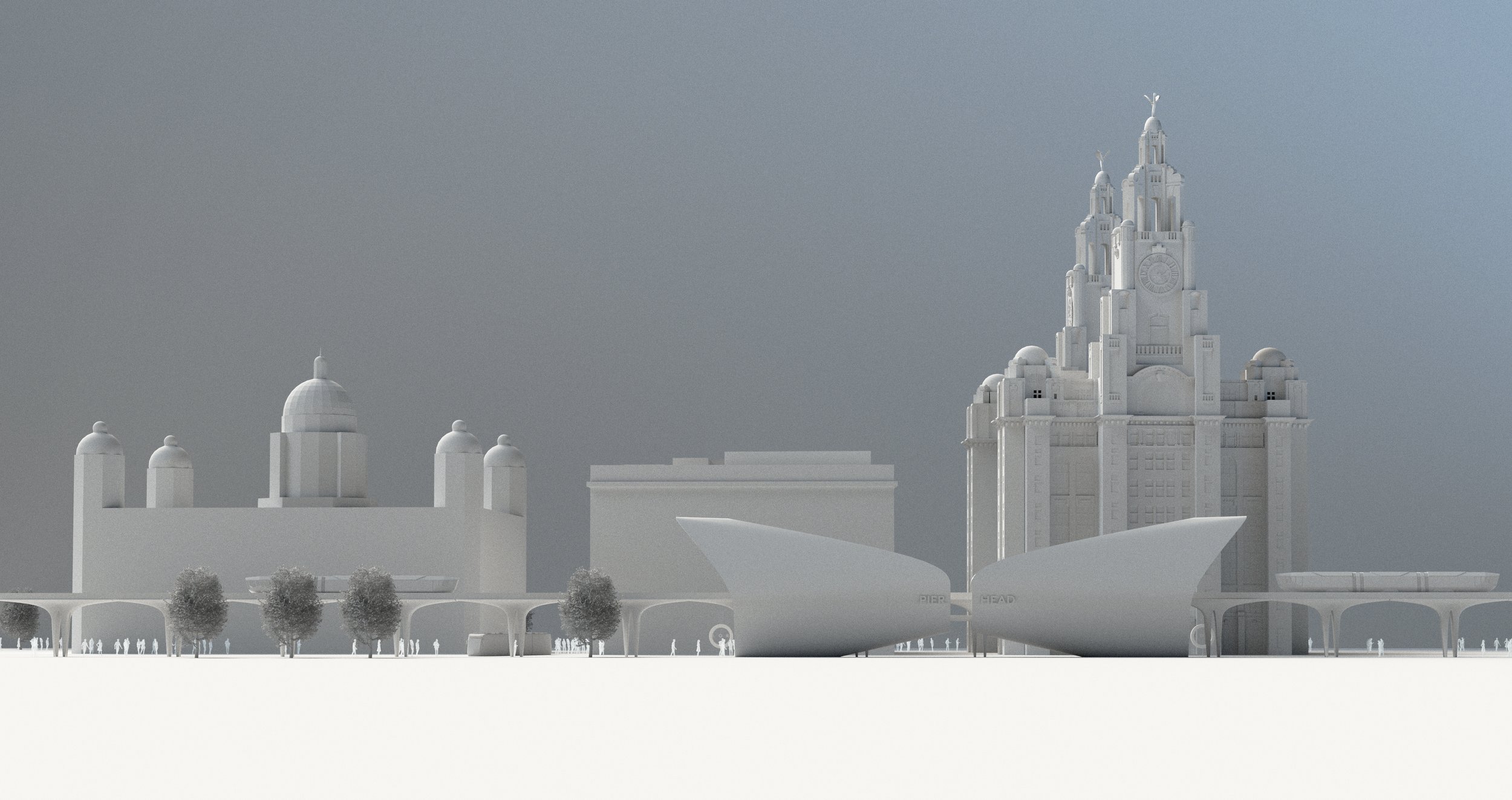
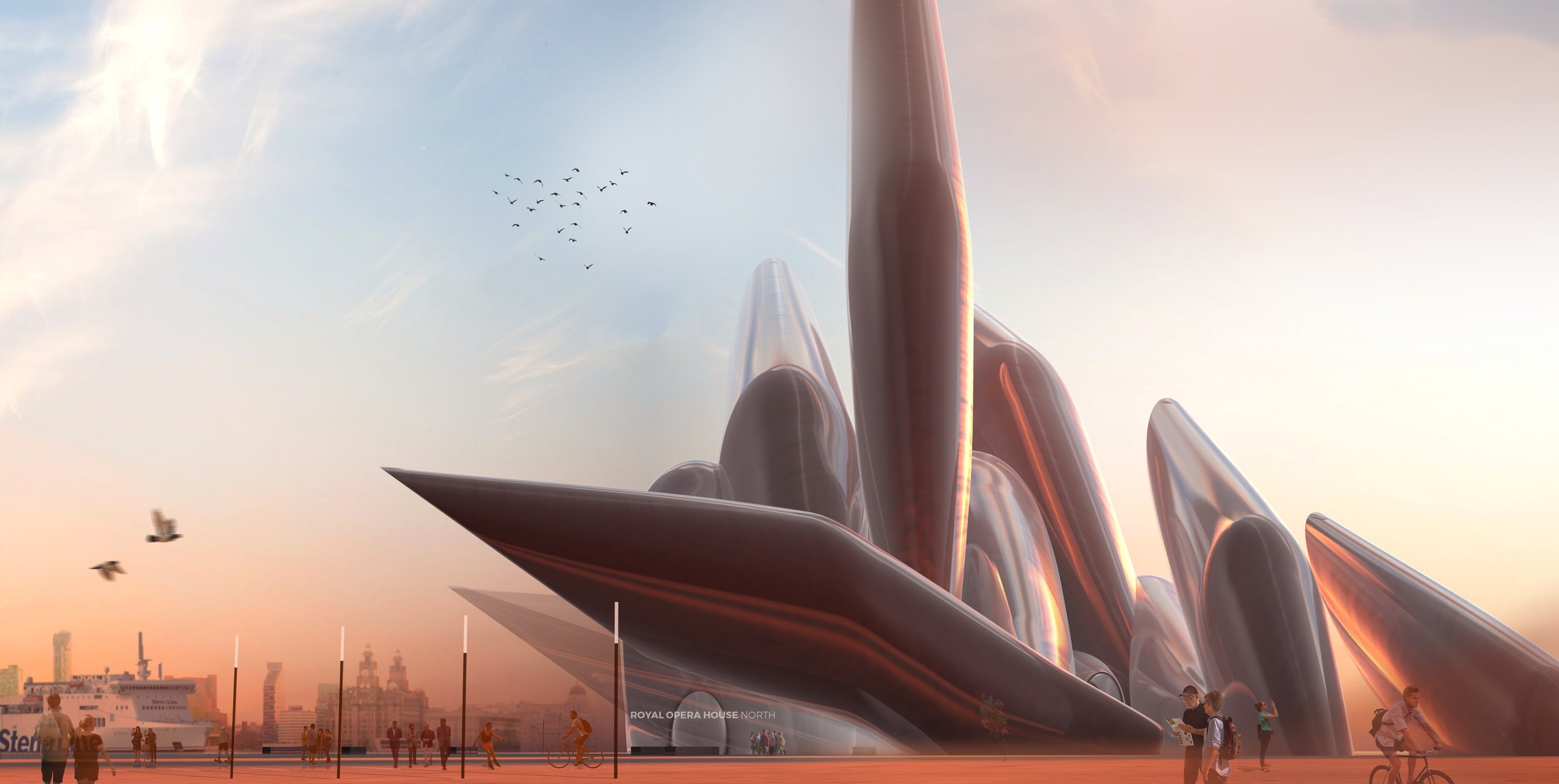
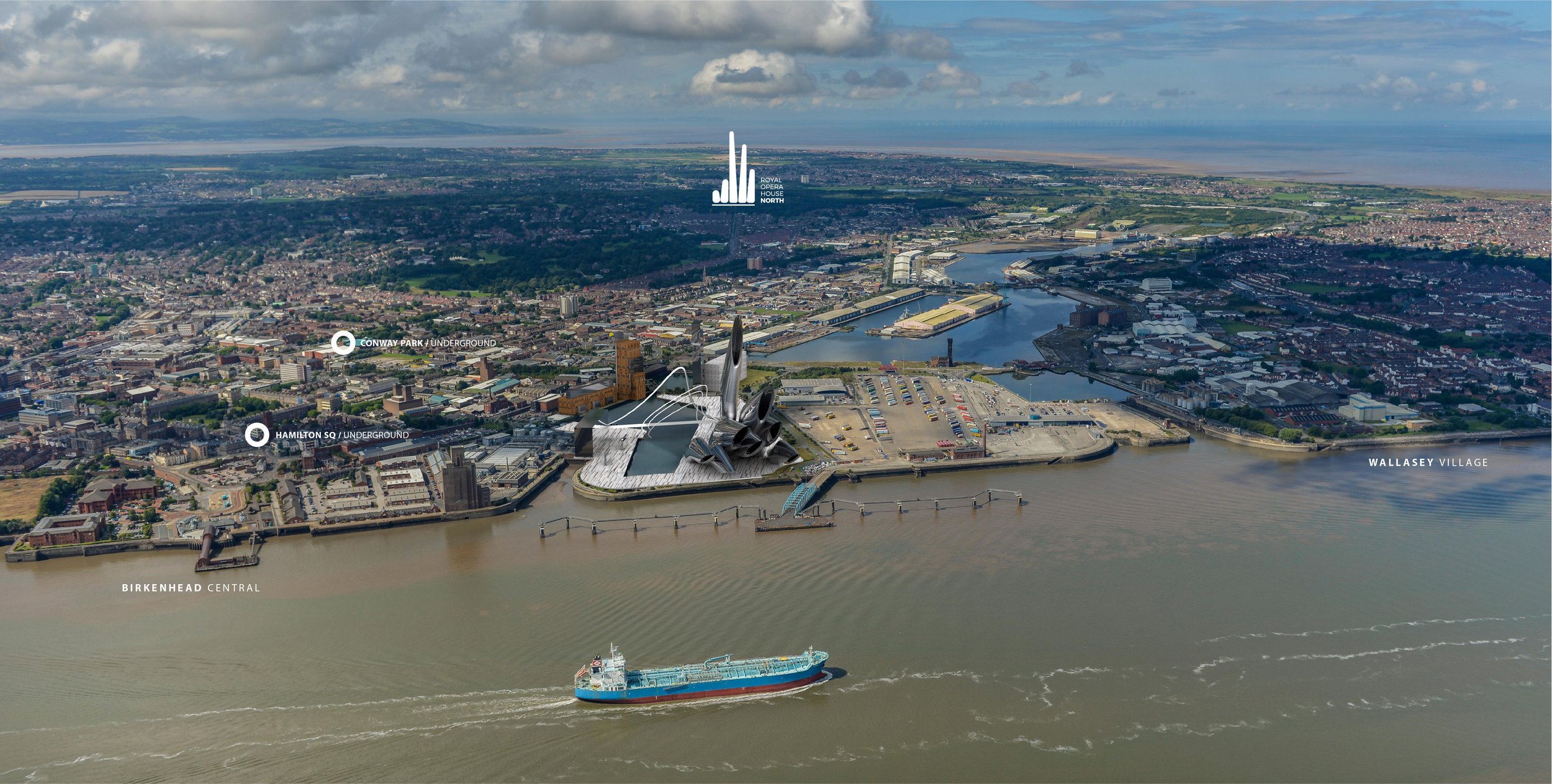
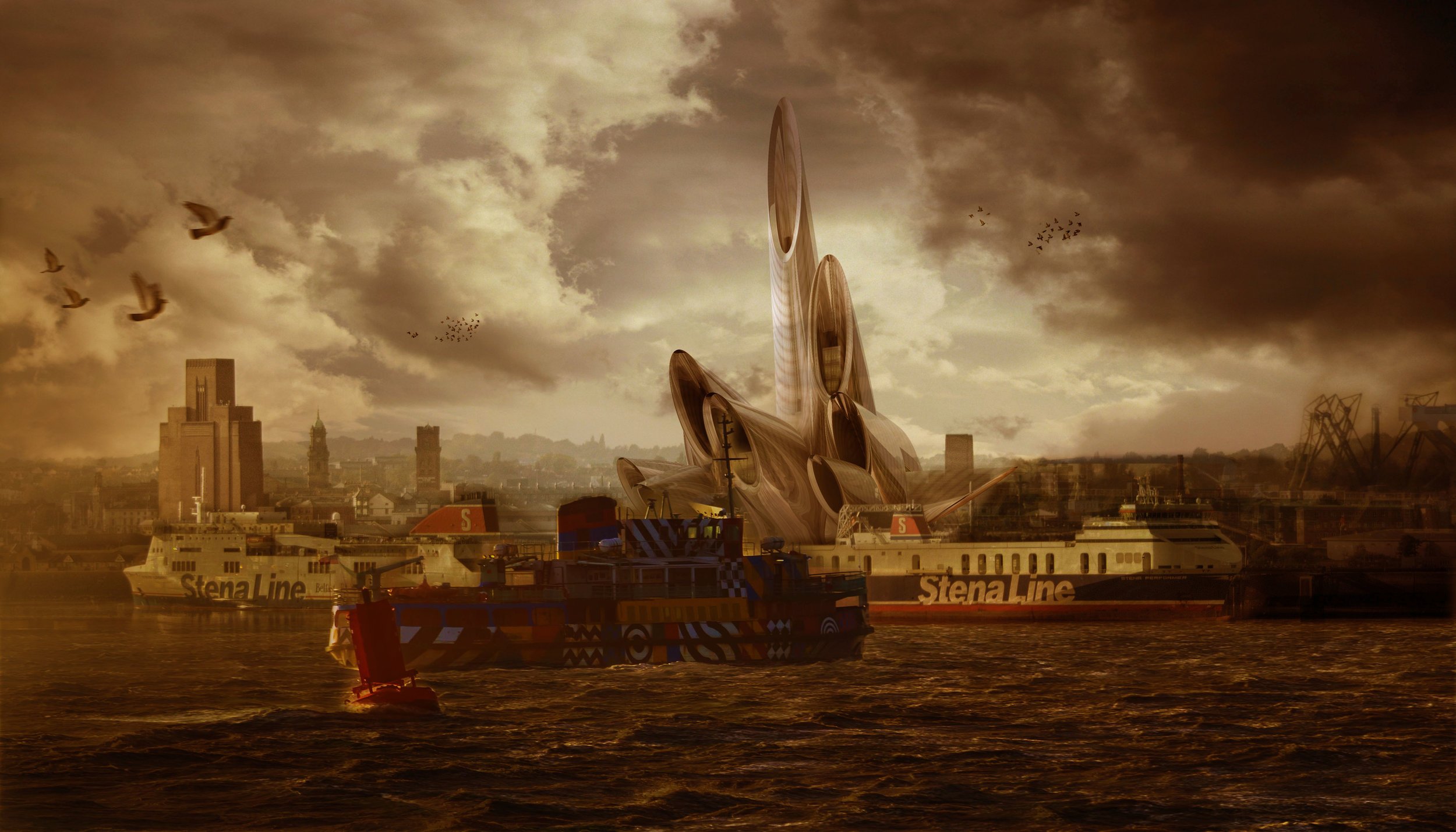
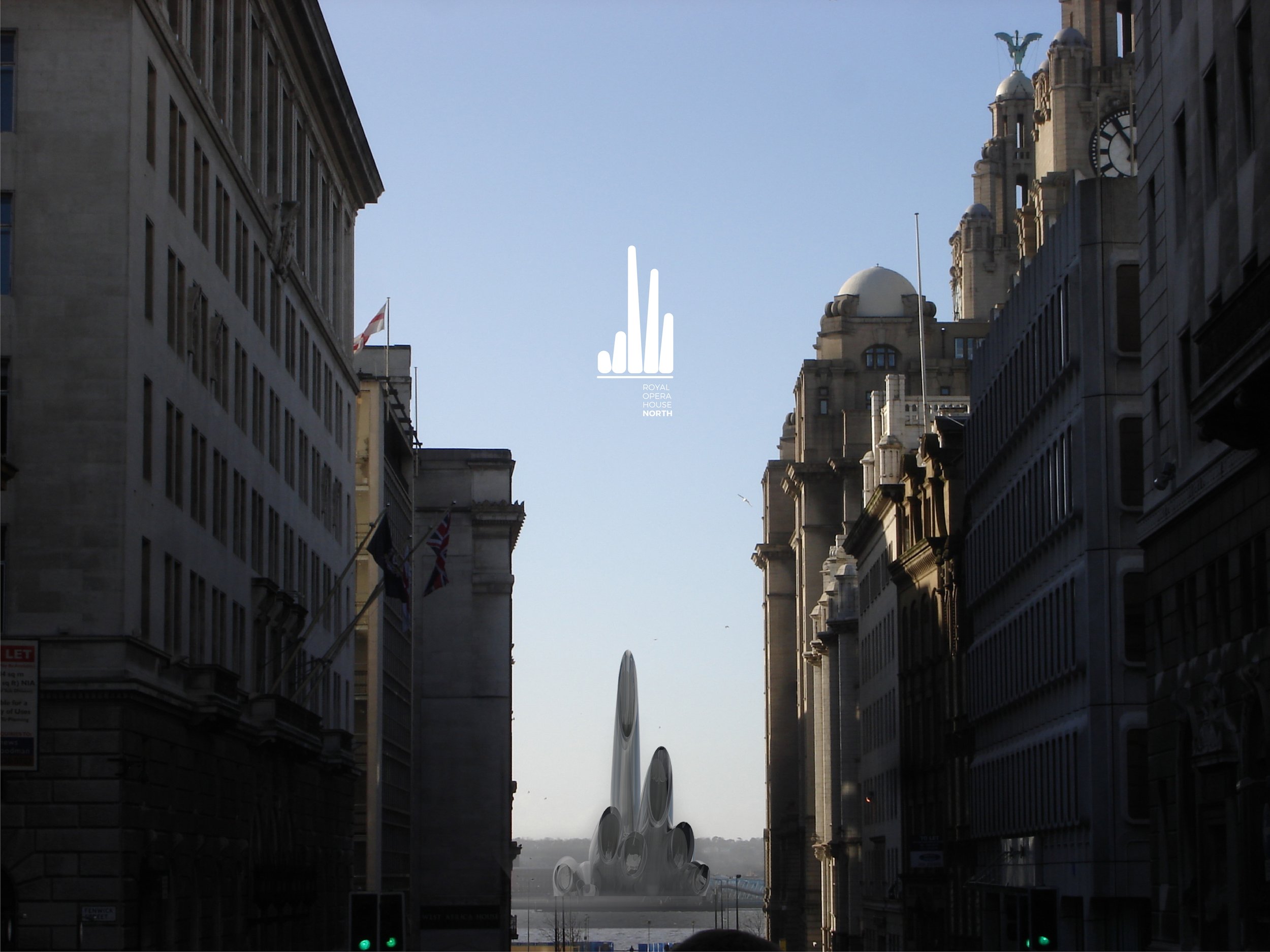
Royal Opera House North & Wirral Cultural Centre
At Liverpolitan, we’ve always believed the Wirral Waterfront to be Liverpool’s great missed opportunity. Overlooking one of the finest riverside vistas in the world, the left bank of the Mersey should be prime real estate, and yet it’s almost apologetically unimpressive – as if frightened to upstage its more famous brother. Surely, we can do better? “People laughed at the idea of Salford Quays hosting the BBC and the Imperial War Museum North,” says Michael, “but with its spectacular setting, the Wirral Waterfront should be aiming higher again.”
Two waterfronts, one city has to be the future but to really make that idea count, at some point we’ll need a significant intervention in the landscape. Wirral Council are doing good work in master planning a new Birkenhead with a better relationship to the river and Liverpolitan is all for it. But to seal the deal, argues Michael, “the Wirral needs something that stands out, something that can be seen from the Liverpool side – something that says ‘Look at me, come over to the Left Bank.’”
Given the 0.7 mile width of the Mersey between Liverpool and Birkenhead, any new landmark structure would need to be huge, gargantuan even. Taller than the 210 feet Ventilation Tower. Possibly taller than the 328 feet Radio City Tower. Cathedral-like in scale and presence. It was along those lines that McDonough put forward this earlier concept for a Royal Opera House North – aligned so that “you can see it as you look down Water Street – the two sides of the river visually connected with an iconic landmark; a catalyst for seeing Birkenhead through new eyes.”
The design is dominated by a series of steel funnels with a glinting chrome façade pointing in all directions of the compass including skyward. They would be wrapped around a central auditorium which could also have uses as a cultural centre exploring the Wirral’s fascinating history from the Vikings to its use as a monastic retreat, not to mention shipbuilding and its colourful background as a smugglers paradise.
‘The Wirral needs something that stands out, something that can be seen from the Liverpool side – that says ‘Look at me, come over to the Left Bank.’
Liverpool HS2
It’s all gone a bit quiet on the High Speed 2 railway project hasn’t it? Maybe that’s a good thing – just get on and build it. But for Liverpolitan, HS2 has always been something of a poker-tell, not so much about the lack of commitment of the national government to invest anywhere outside of the south – which to be honest, we can all take for granted. No, what HS2 really reveals in full technicolour is the shallowness of Northern solidarity – some places, most notably Manchester and Leeds are consistently favoured over others like Liverpool and Newcastle. Despite the sweet words of ‘King of the North’, Andy Burnham, arguments about agglomeration are forever used to draw money and opportunity towards these investment blackholes and away from everywhere else. And HS2 has been the smoking gun. More’s the pity that Liverpool’s own leaders have been too foolish to notice (or they never cared).
When the Conservative government announced the Integrated Rail Plan for the North and Midlands in late 2021, the media was full of a wailing and gnashing of teeth. Cutting HS2’s eastern leg to Leeds and scaling back plans for Northern Powerhouse Rail was seen as more evidence of the perfidiousness of London and Whitehall. Right on cue, Liverpool’s often hapless Metro Major Steve Rotheram, joined in the venting, complaining that “we were promised Grand Designs, but we’ve had to settle for 60 Minute Make Over.”
Not for the first time, a fair reflection of Liverpool’s own particular interests was absent, but with the help of railway campaigners like Martin Sloman and Andrew Morris of 20 Miles More, Liverpolitan spotted it. The truth was, the plan might have been less good for Leeds and Manchester but it was better for Liverpool. Fresh high speed track was going to be laid closer to the city in a dedicated spur that would relieve capacity constraints and increase the scope for an expansion in freight services. In addition, the need to widen the narrow throat entrance to Lime Street was also finally acknowledged. Hurrah!
‘What HS2 really reveals in full technicolour is the shallowness of Northern solidarity – some places, most notably Manchester and Leeds are consistently favoured over others like Liverpool and Newcastle.’
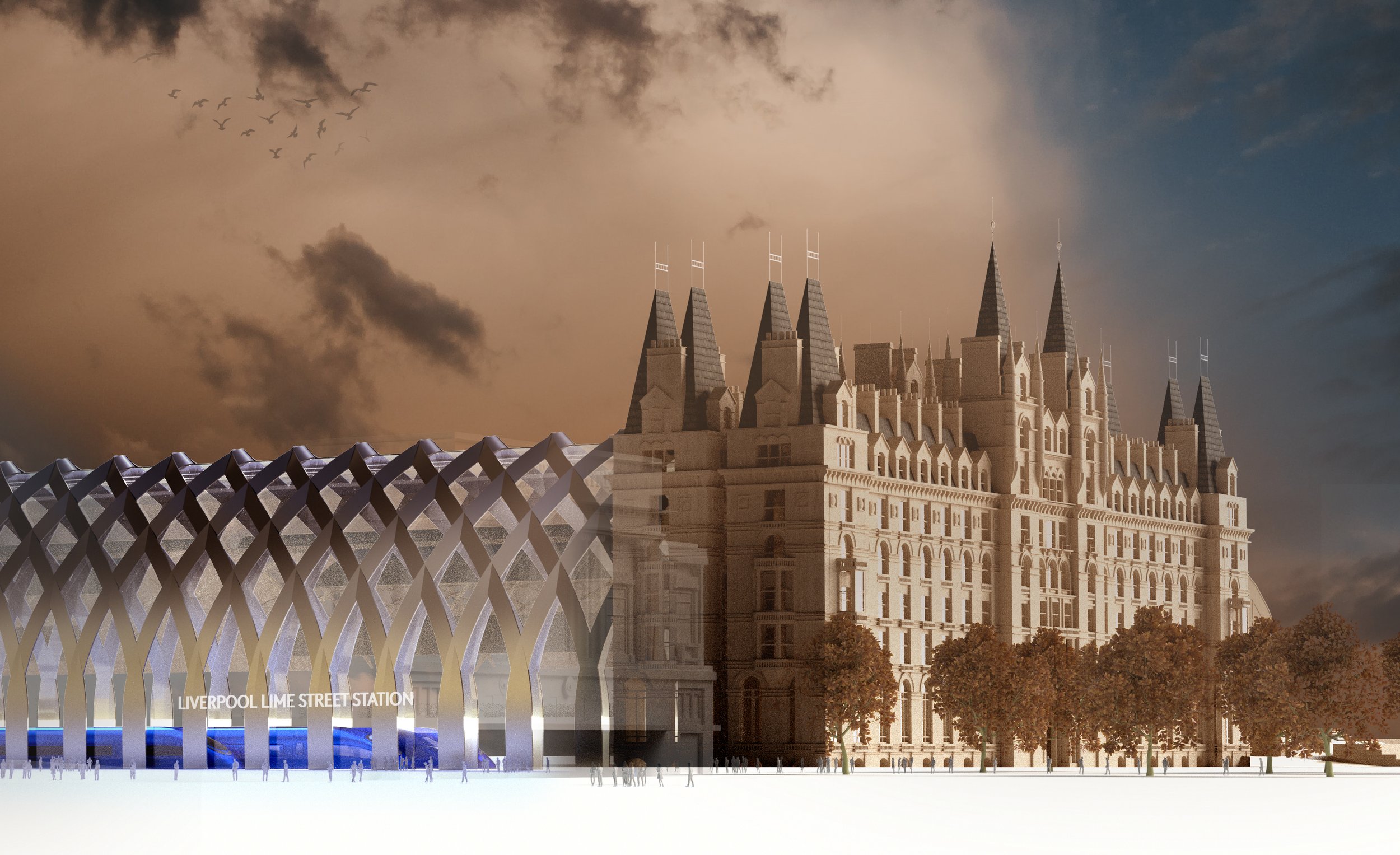
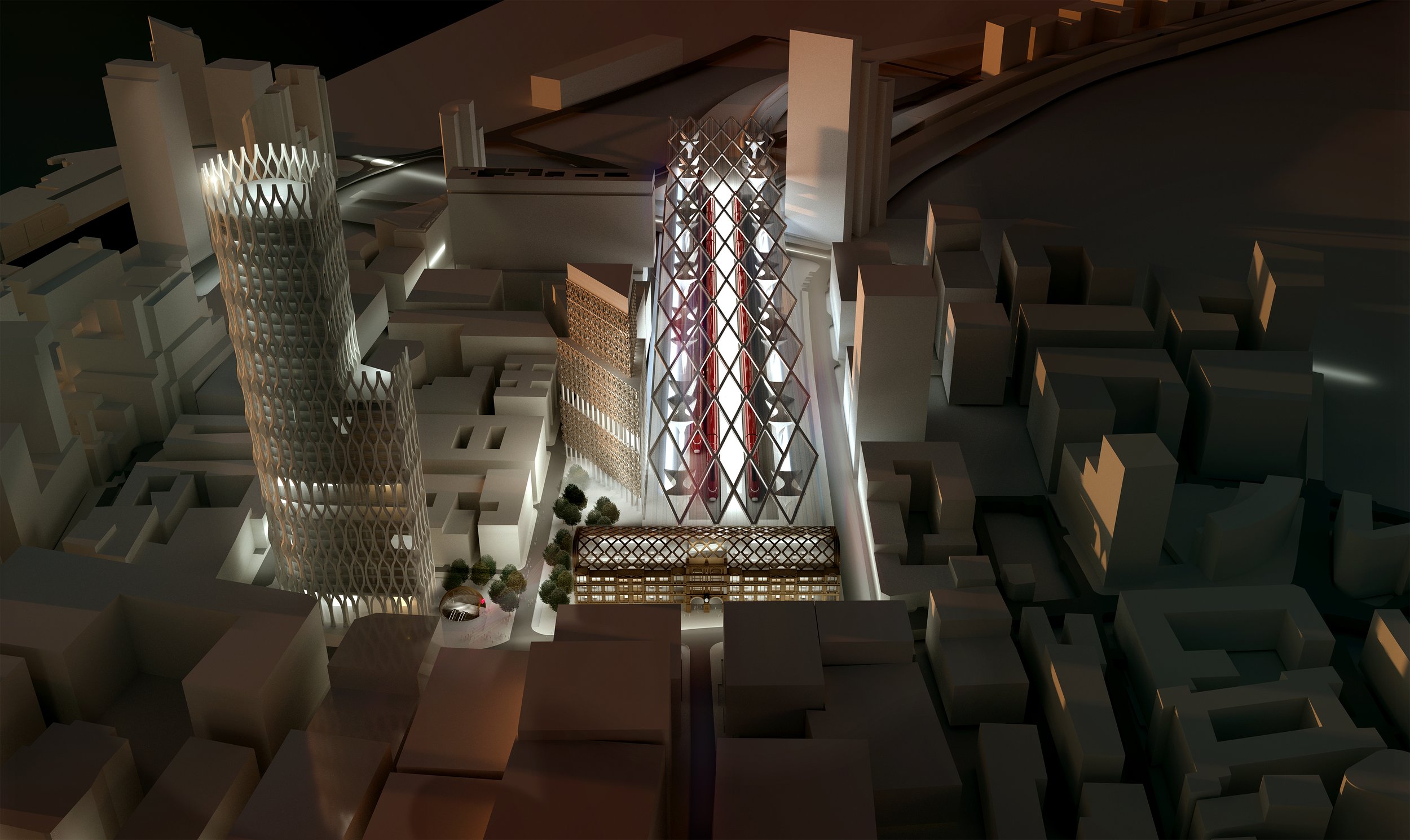
Still, wanting the best for Liverpool means building new track all the way into the city centre serviced by a full specification HS2 station. By the way, what happened to the commission set up by Steve Rotheram in March 2019 and announced with full fanfare at the MIPIM Property Exhibition, which chaired by Everton CEO Denise Barrett-Baxendale, was going to choose between 2 possible locations for a new “architecturally stunning” HS2 station in the city centre as well as 5 routes in for the track? Quietly dropped?
Focusing on the most likely outcome of a redeveloped Liverpool Lime Street, Michael has put together some outline designs, which incorporated the grade-II listed Radisson Red Hotel (previously the North Western Hotel) as the main entrance to the station.
To read Liverpolitan’s cutting dissection of HS2 and the Integrated Rail Plan for the North and Midlands, check out ‘HS2 – A Liverpool Coup?’ by Michael McDonough and Paul Bryan
Or to read Martin Sloman’s examination into the options for a city centre station, try ‘Lime Street or Bust? The Options For Liverpool’s HS2 Station’
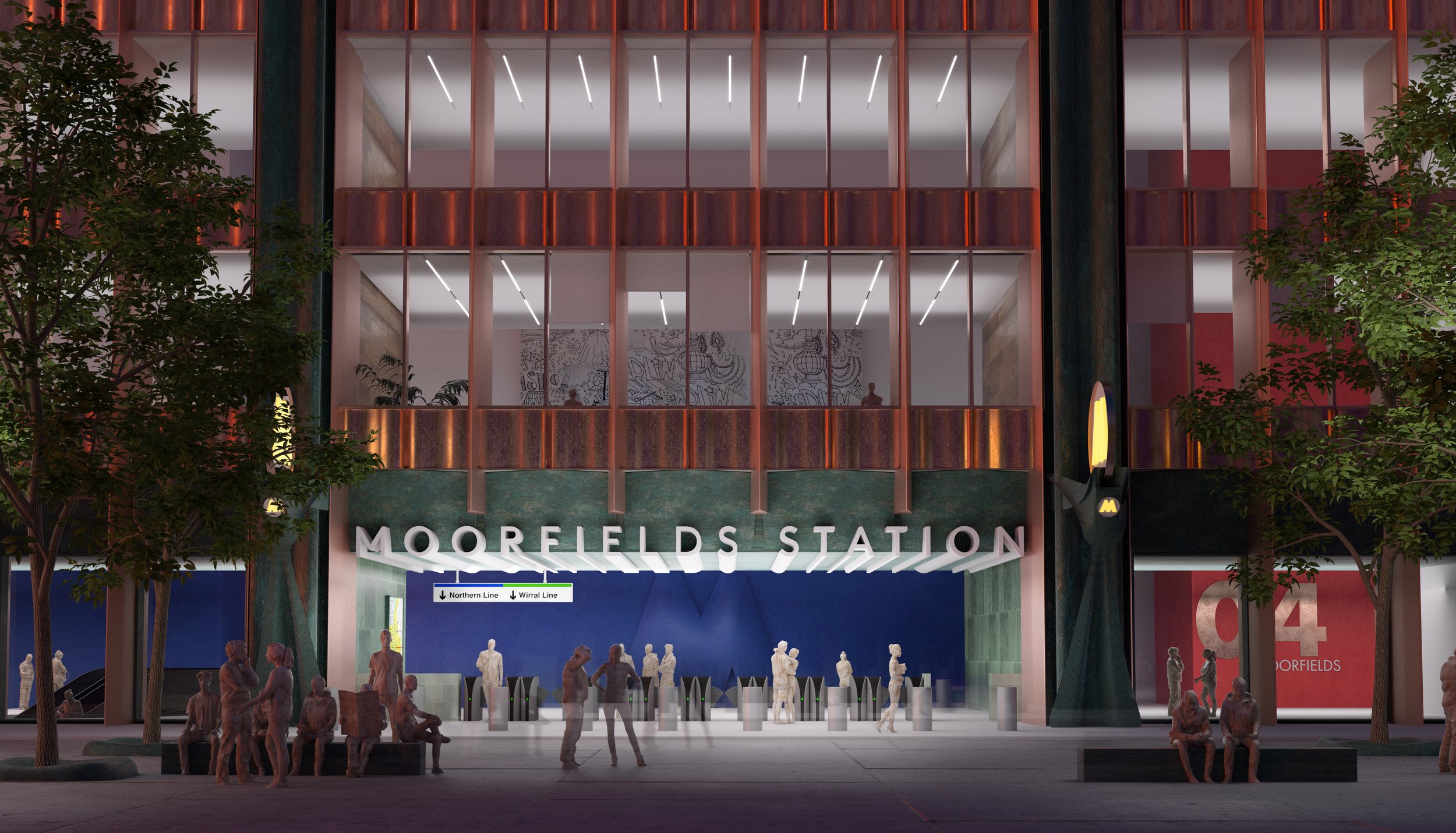
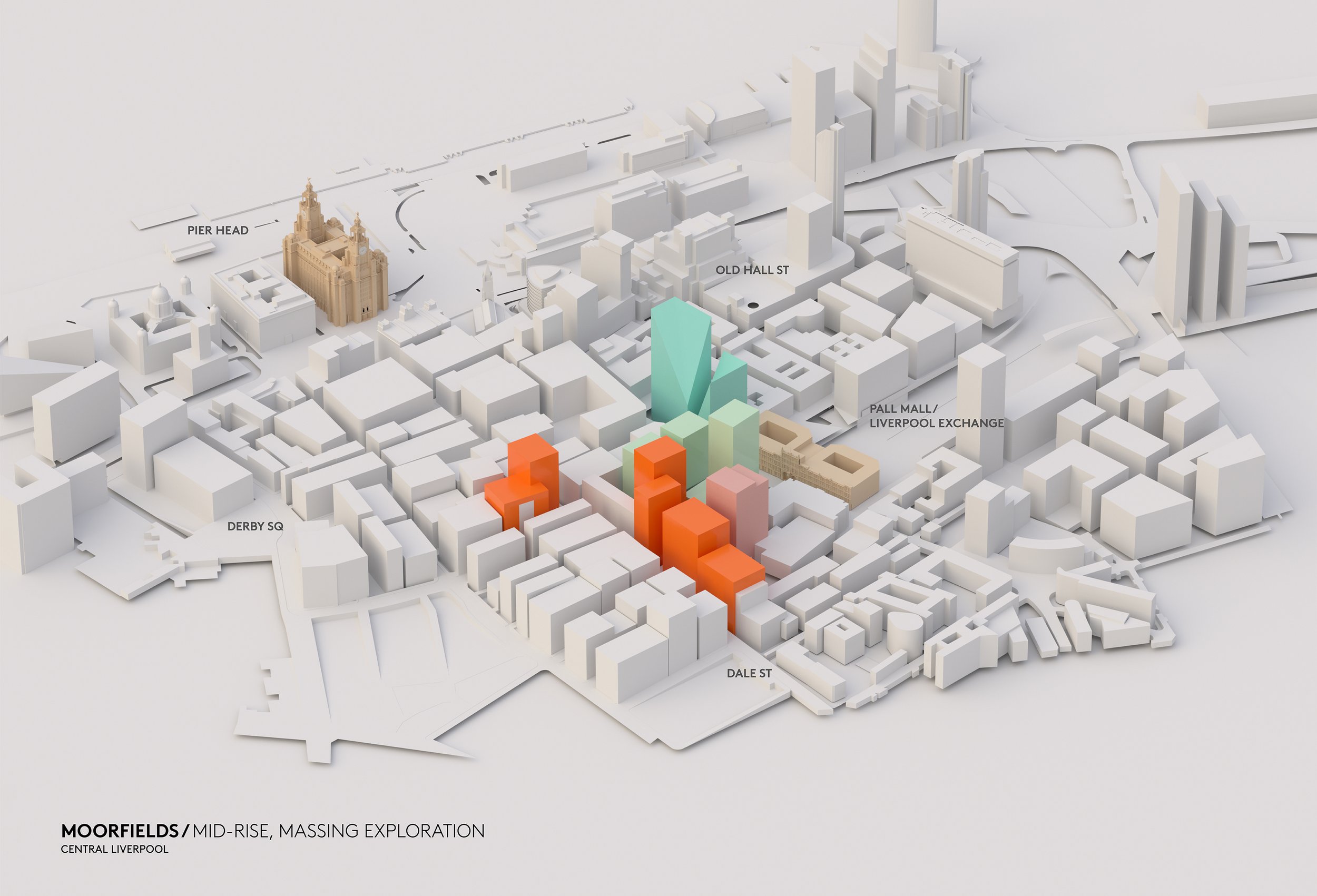
Moorfields and the Commercial District
Back in March 2023, Liverpolitan tweeted about the state of Moorfields, which we described as “a regrettable symbol of Liverpool's down at heel CBD.” We noted that the area is littered with dereliction, empty office buildings and signs of homelessness, and asked the question, “Have we become so used to this embarrassing patch that we no longer see it as failure?”
The tweet received almost 45,000 views and provoked a whole host of online conversation with the issue later picked up by the Liverpool Echo. Councillor Nick Small, who after the recent local elections is now the city’s Cabinet Member For Growth and the Economy, got involved, agreeing that the site needs to be developed. There was some discussion about whether robust plans for the area were in place already as part of the City Centre Local Plan and Strategic Investment Frameworks (SIFs). But mostly, to the extent that the local BID or the Council have acknowledged the issue, action on the ground seems in short supply.
To some extent, the lack of regeneration may be an issue of plot owners sitting on parcels of land and waiting for a payday, but as a subsequent squabble between Merseyrail and the Council over who was responsible for cleaning the grotty Moorfields escalator showed, a lack of concerted coordination between agencies leaves ample scope for things to fall between the cracks.
Moorfields is littered with dereliction, empty office buildings and signs of homelessness. Have we become so used to this embarrassing patch that we no longer see it as failure?
Michael McDonough argues that Moorfields is another of Liverpool’s great missed opportunities and it’s hard to disagree. The area’s city centre location, great transport links, and historic setting within the traditional heart of Liverpool commerce, should with the right support, allow it to live again. “The whole area needs re-invention and the drift towards noisy bars and tourism serves to cheapen its prospects,” says Michael. He claims that demolishing the rotten Yates Wine Lodge should just be the start. “Moorfields can handle density and scale and is the perfect place to rebuild Liverpool’s grade-A office offer” centred around the idea of prestige and talent.
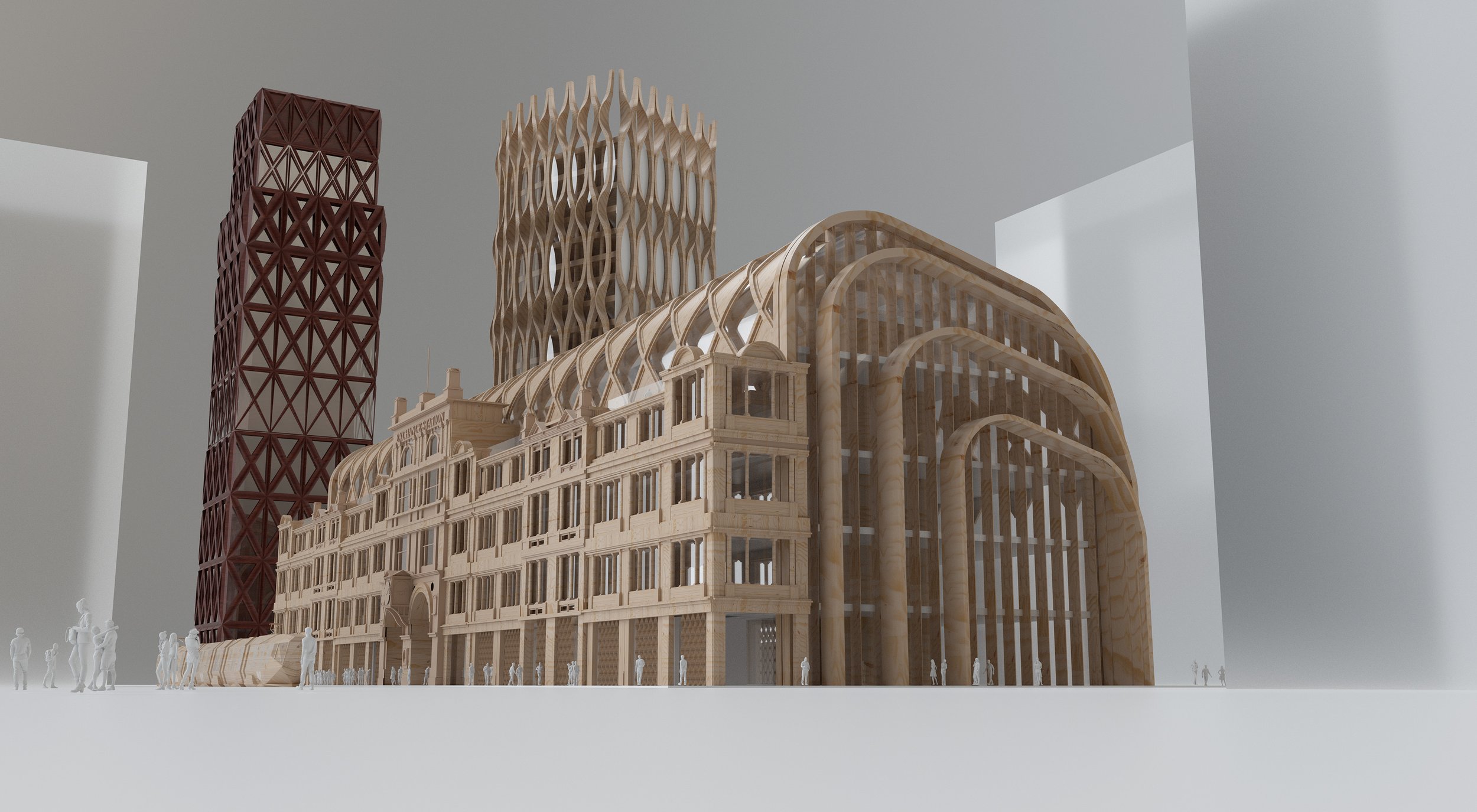
In these visuals, Michael wanted to rebuild the entrance to Moorfields Station with mid-rise commercial office space above – no more going up to go down. He also took a stab at upgrading the former Exchange Station offices, which “may have been grand from the front, but from the rear leave a lot to be desired” – failing to properly address the park that will hopefully one day be re-instated as part of new public realm within the wider Pall Mall development.
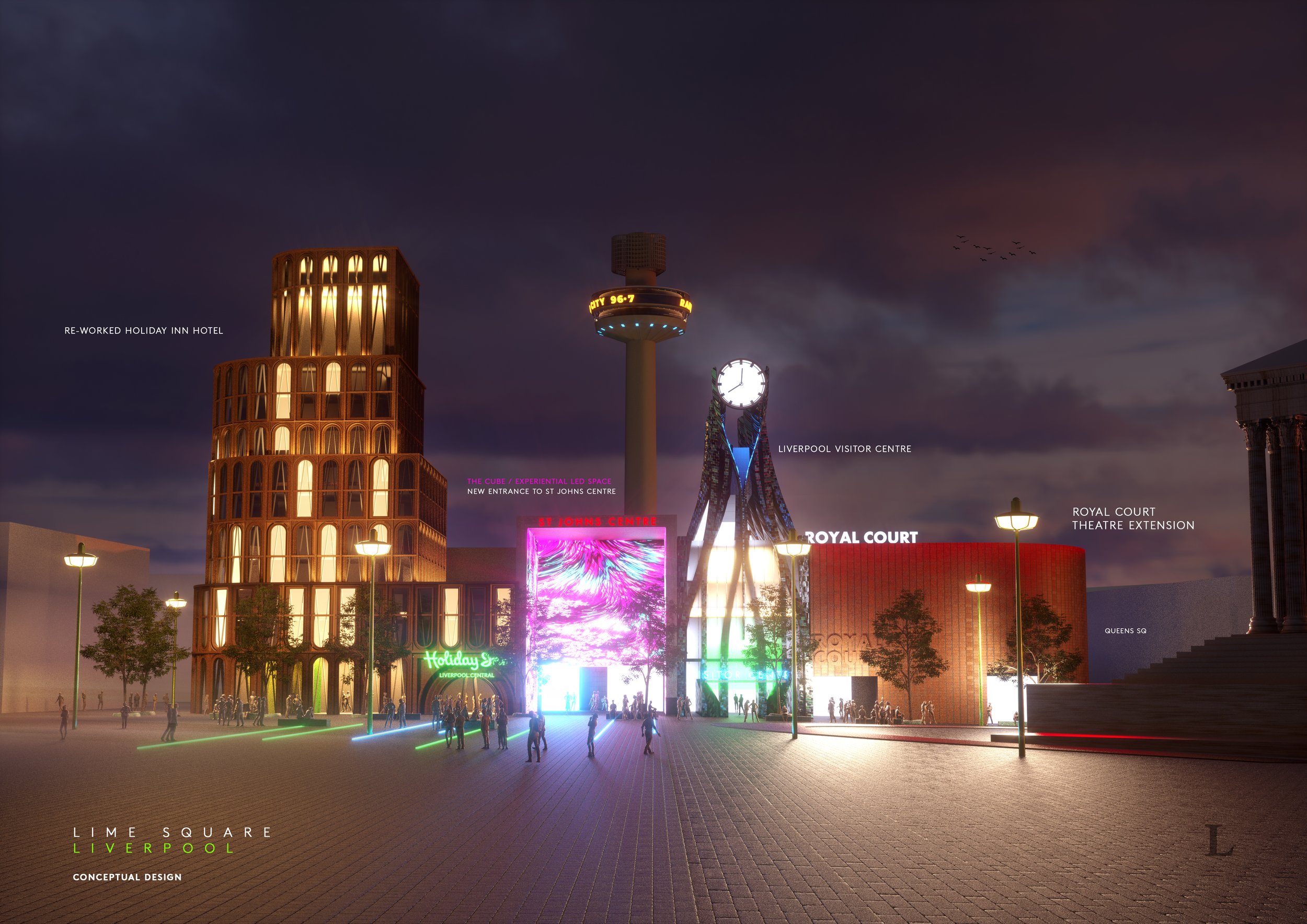
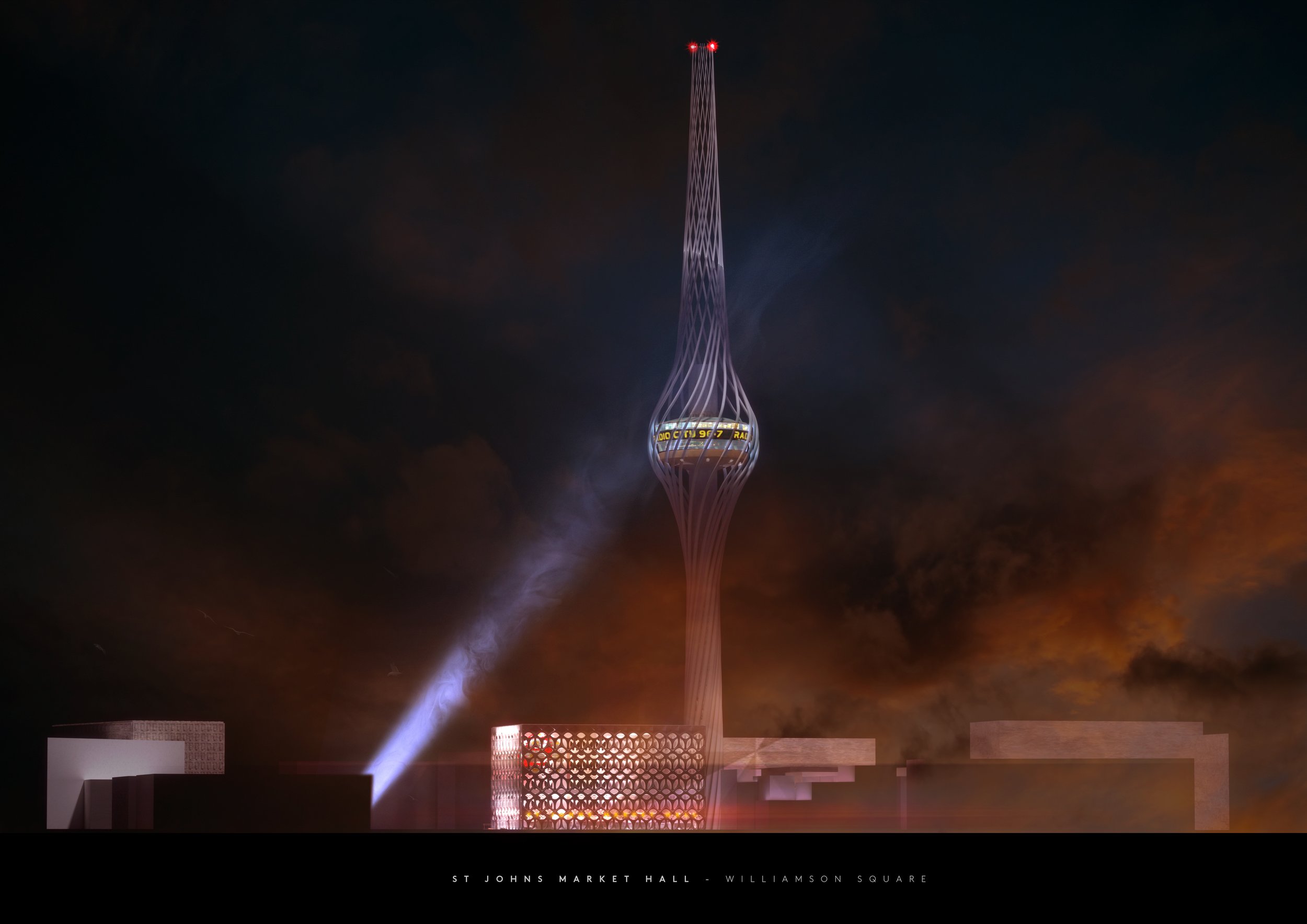
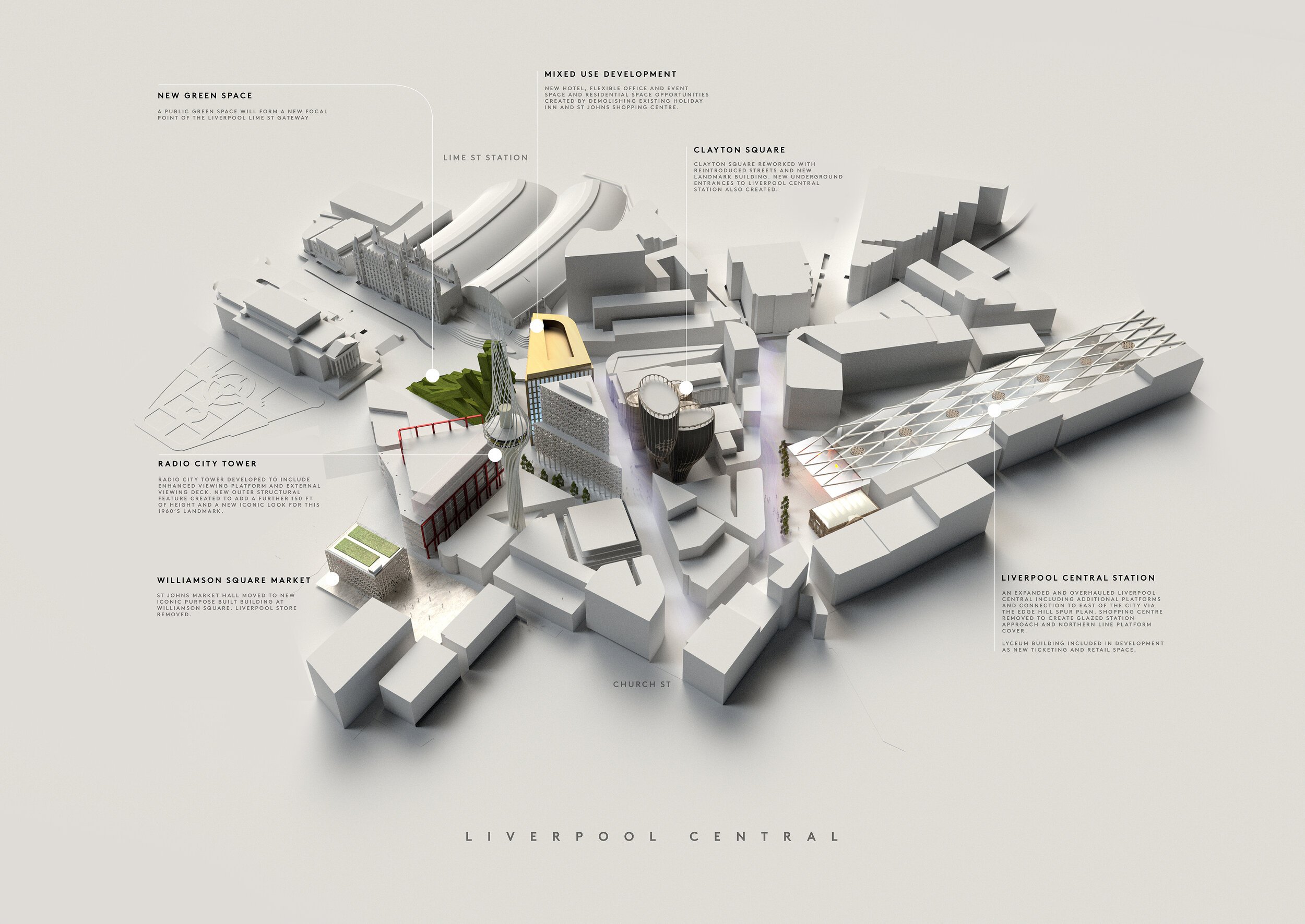
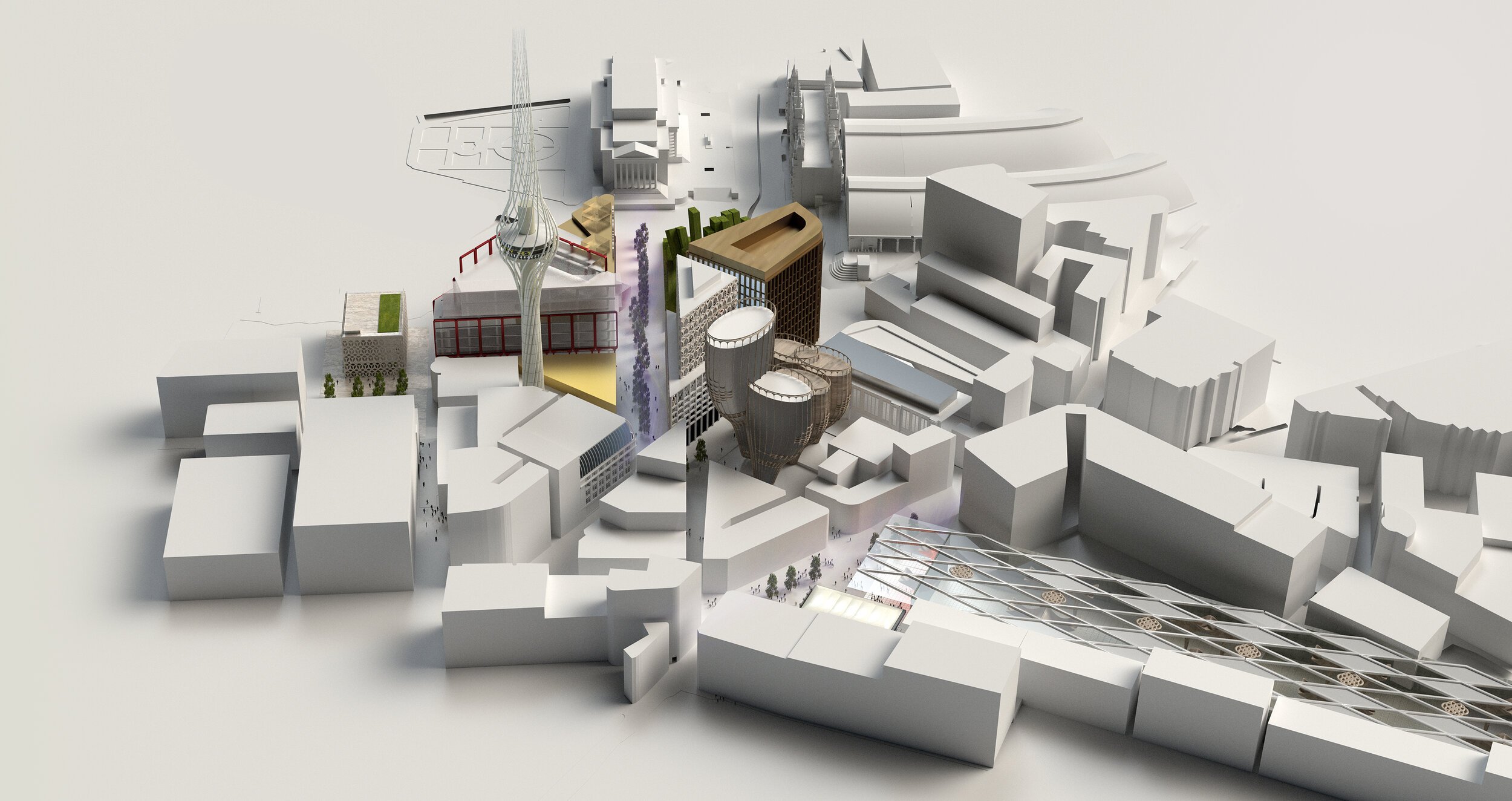
St Johns and Central Liverpool
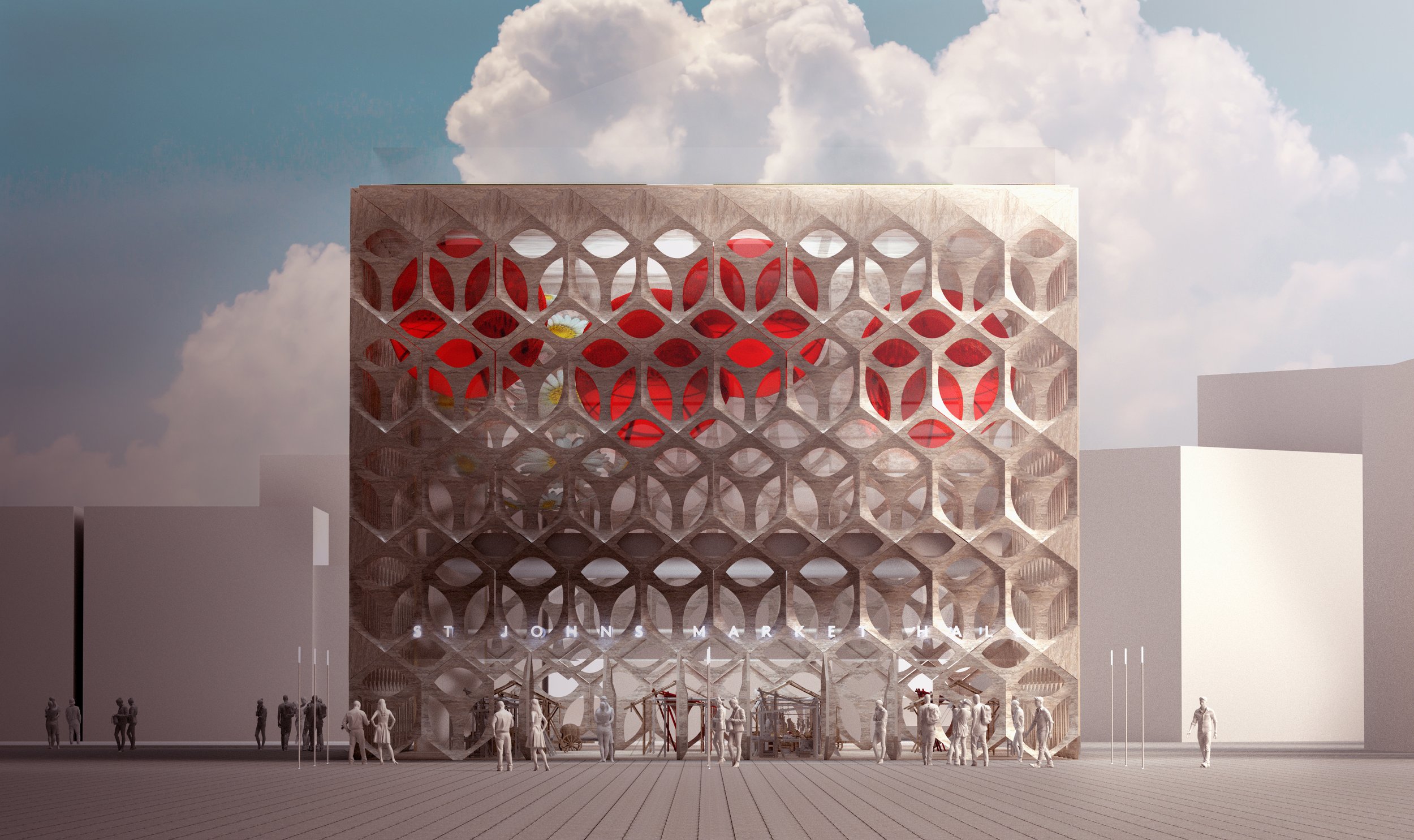
Far, far and away McDonough’s biggest bugbear with Liverpool’s built environment has to the St Johns Shopping Centre. We know it’s commercially successful and last time we looked it had a 97% retail occupancy rate. It clearly fills an important niche within the city’s shopping offer with its cheaper rents for retailers. But damn if isn’t an ugly pig of a building (no offence to our porcine brethren). Arriving at Liverpool Lime Street, that’s the first thing you see. Talk about first impressions. Squatting over a network of old streets and the site of what would be today, if it hadn’t been bulldozed, a much valued Victorian market, Michael believes St Johns is a “dated lump of a building that acts as a physical and psychological barrier between London Road and the rest of the city centre.” It’s not a stretch to suggest that St Johns has played a role in the former’s decline. Repeated, half-hearted attempts to patch the shopping centre up have failed and its blue plastic blanket and struggling traders’ market are a testament to “a succession of bad planning decisions going back fifty plus years.” A lasting solution to all of these problems, says Michael, “requires demolition.”
The images Michael has put together here are a collection of different attempts to reinvent this “ugly and misfiring section of Liverpool.” The main driving force behind his designs is a desire to remove this “lumpen barrier” and re-stitch together our centre “in a more permeable way that evokes expressions of pride rather than cringes.” Michael wants to see a much better front door to Liverpool Lime Street – our city’s once grand hello and goodbye point. He’d like to replace this “parody of the city’s greatness” with something more iconic and ambitious.
‘St Johns is a dated lump of a building, its blue plastic blanket and struggling traders’ market a testament to a succession of bad planning decisions going back fifty plus years.’
The eagle-eyed might spot the use of neon and a prominent clock tower as a modernised callback to what the site has lost. As Michael says, “we can’t always recreate the past but we can be inspired by its best bits.” He’s also given the Grade 2-listed but still a bit ugly, Radio City Tower, a makeover, adding an elegant polished steel lattice of radiating lines which add height, fluidity and tricks of light to recast a regional landmark into one of world significance.
Read more about Michael McDonough’s vision for St Johns in the Liverpolitan feature, A New Central Liverpool.
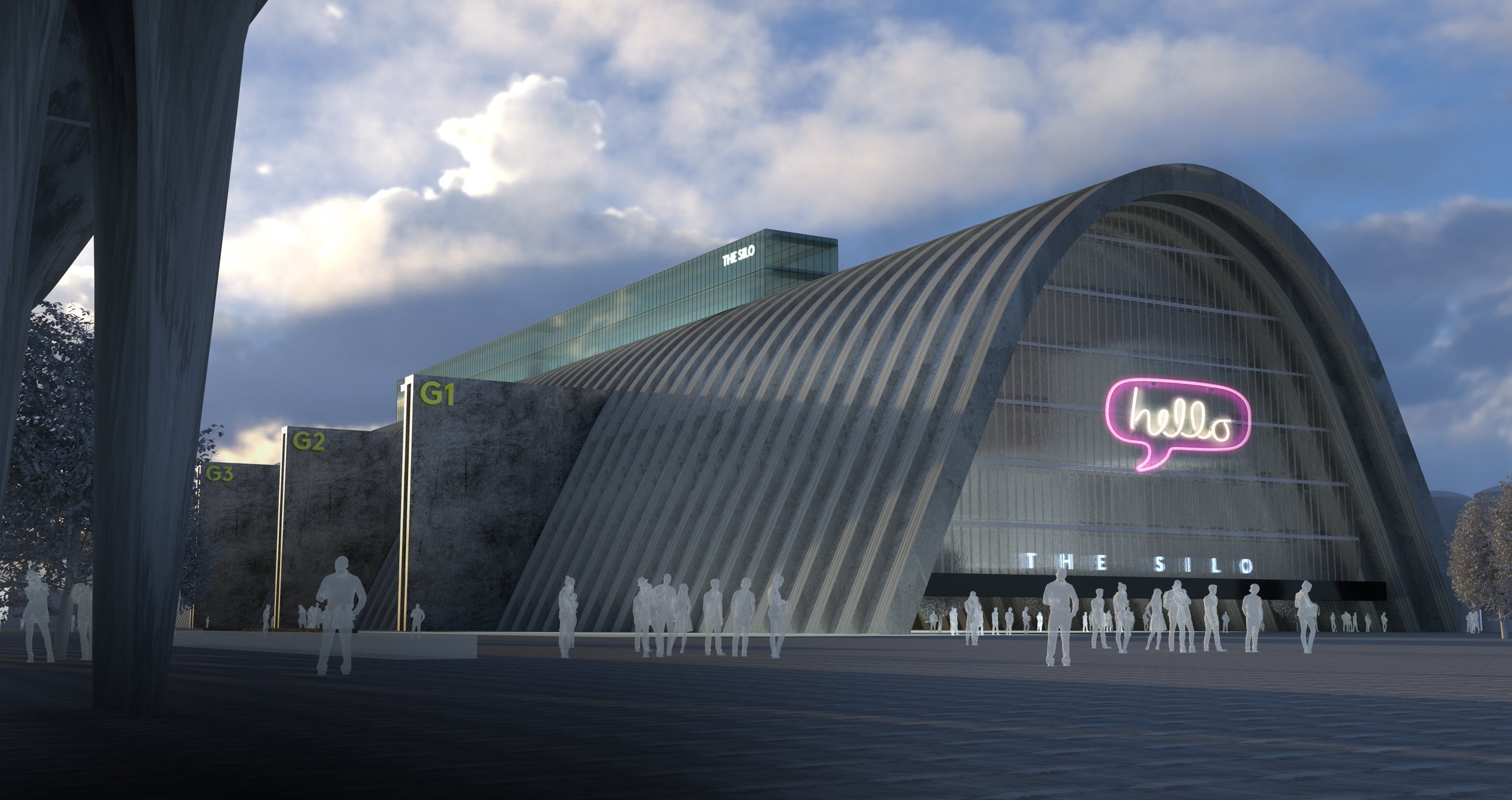
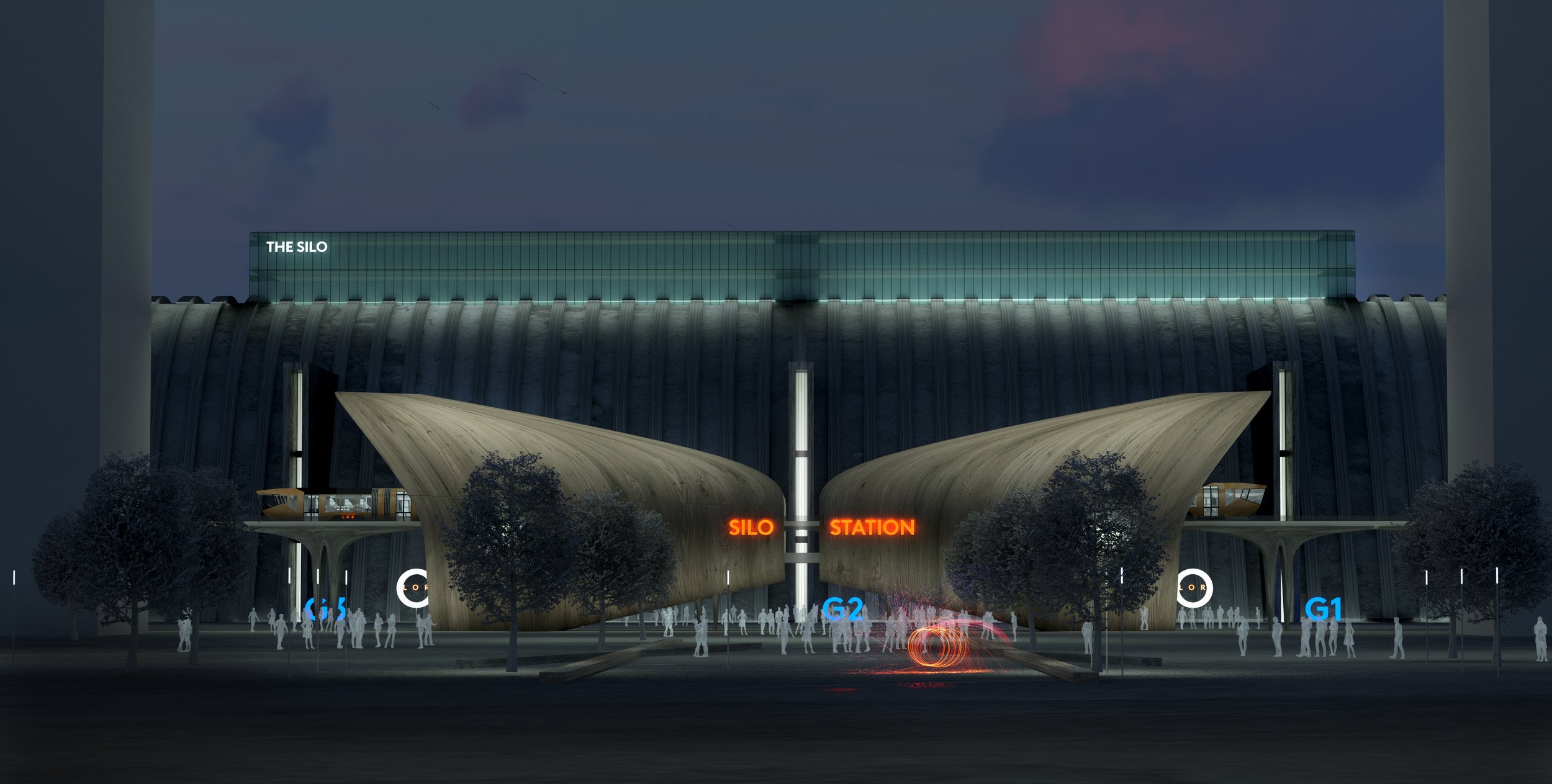
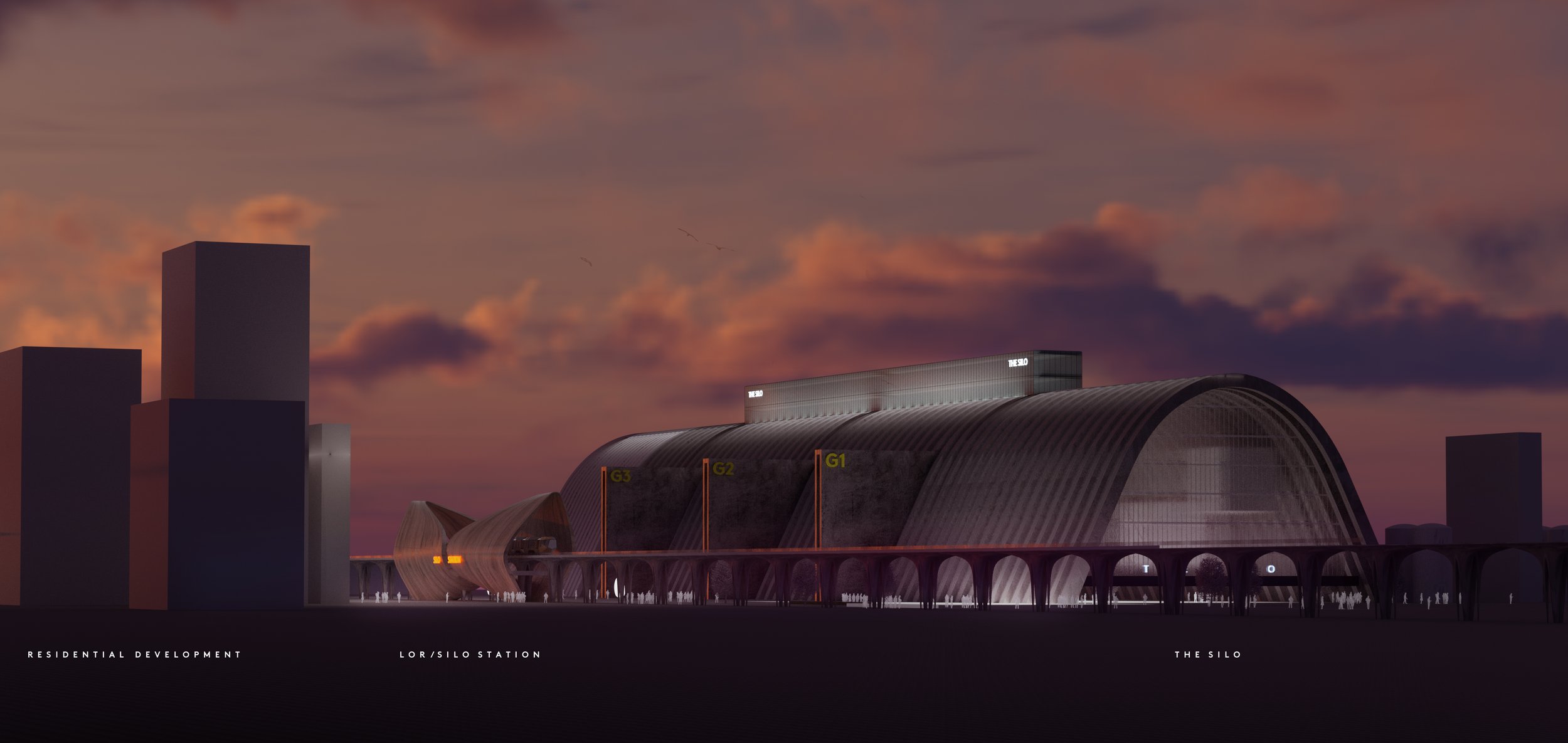
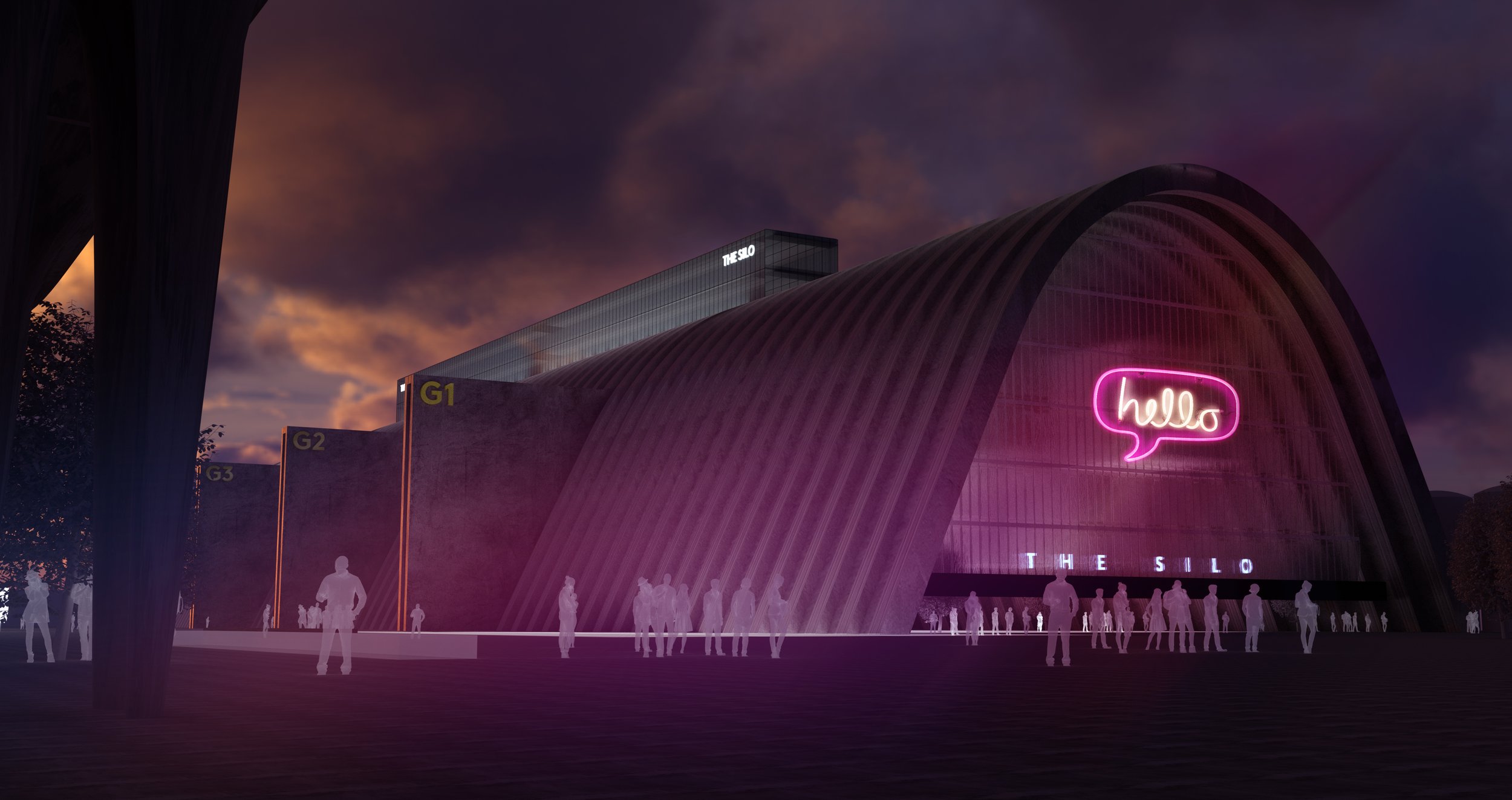
The Silo
The former grain silo in the north docks is one of Liverpolitan’s favourite buildings in Liverpool. If it was just a little further south, closer to the Tobacco warehouse and Bramley Moore, we could imagine it being repurposed as a truly iconic, high capacity arts, events and business hub. However, the silo is located deep within the working part of the dock estate with industrial infrastructure all around it, so that idea is likely to remain a dream. Still, just imagine what could be done with this incredible structure. For McDonough, the project would “represent a development challenge similar to how London’s Bankside Power Station was transformed into the Tate Modern.”
For these visuals, Michael has re-imagined the space as a media industry hub – with film, TV and radio studios and education space for our universities – “a back-up plan in case the Littlewoods Film Project doesn’t deliver.” There would also be a theatre venue, gallery space and office facilities for the production sector – which he describes as “the perfect tonic to act as a catalyst for the regeneration of North Liverpool.” Another possible use, he suggests, might be a central hub for burgeoning logistics businesses if the new Freeport ever takes off. As you can see, Michael has taken the liberty of re-instating the Liverpool Overhead Railway, with ‘Silo Station’ ready to whisk visitors straight to the doorstep.
‘What Michael is attempting to do with these designs is to remind the city that it’s capable of bigger ideas, capable of re-imagining itself, capable of statement architecture, and capable of challenging its city rivals.’
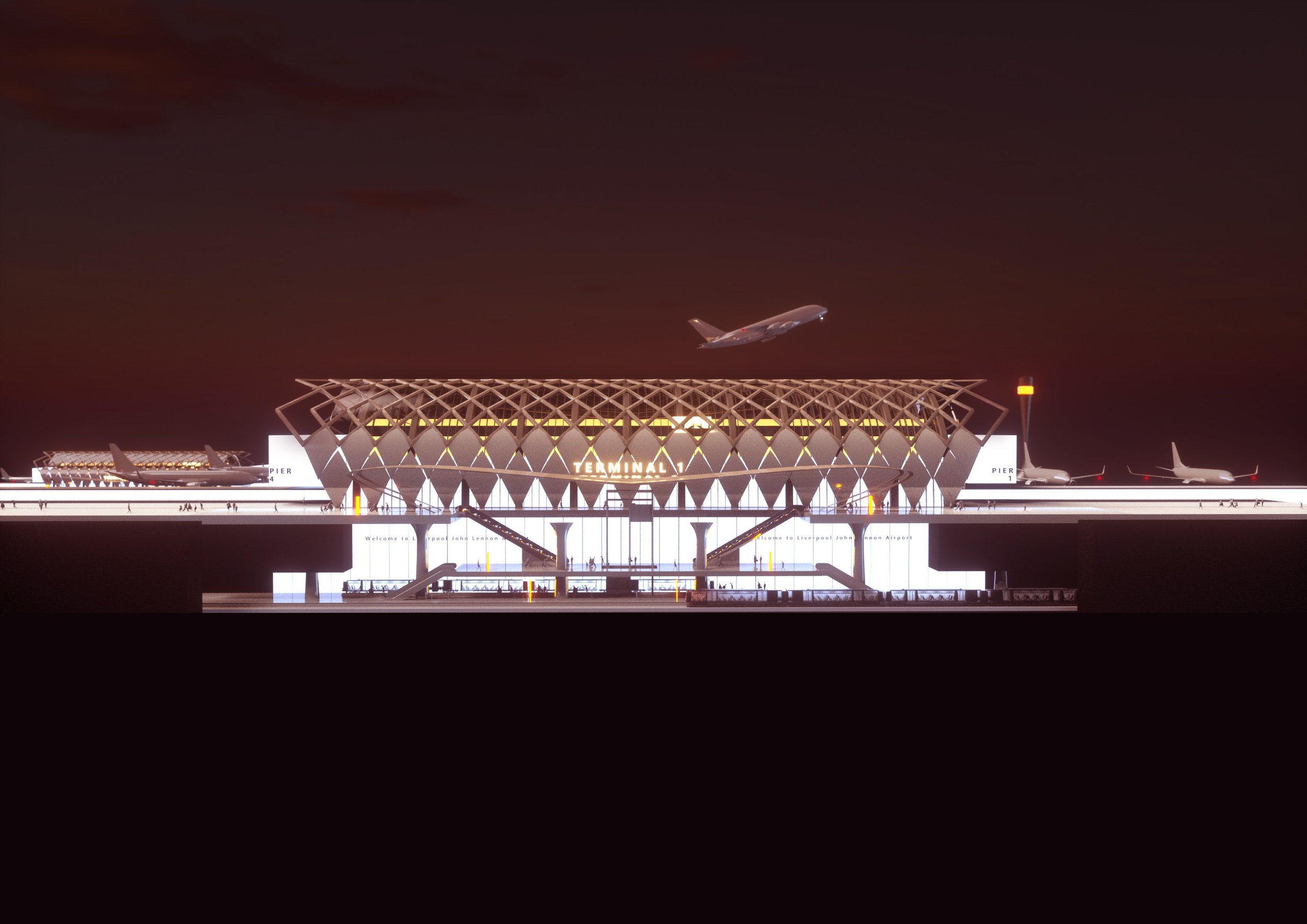
Liverpool John Lennon Airport
Not for the first time, Liverpool John Lennon Airport finds itself in a strange position. Back in the years following World War 2, JLA (minus the Beatles moniker) lost its opportunity to become the north’s most important airport when the Ministry of Defence, which had requisitioned it for the RAF, sat on the asset while its Manchester rival grew. It’s been an uphill struggle ever since.
Not that Speke Airport, as some still call it, hasn’t had its days in the sun. For a time in the early 2000s, Liverpool was THE favoured location for budget airlines in the northwest as passenger numbers ballooned from 0.6 million in 1997 to 5.5 million in 2007. That growth stalled as its much larger rival came to its senses and stopped turning its nose up at budget travellers. Still, JLA has remained a valuable strategic asset for the city, and despite the devastating blow that Covid dealt to its passenger numbers and its finances, the airport is making a solid recovery. Finally free of the dominant stranglehold of Ryanair and Easyjet, the airport is now diversifying its offer, attracting new airlines such as Lufthansa, Air Lingus and Wizz Air. And JLA continues to pick up a steady stream of awards for the efficiency of its operations, where queues tend to be largely absent.
Sad then, that Liverpool Airport has found itself consistently under attack in recent years from local environmental activists such as Liverpool Friends of the Earth and the Save Oglet Shore campaign group, who appear to want to make an example of it, by opposing all possible expansion. In fact, it’s been pretty clear in Liverpolitan’s own Twitter debates with these groups that there are those who would like to see the airport closed altogether – its miniscule contribution to the nation’s CO2 output too much for some. Others claim the farmers’ fields to the south are too ecologically important to lose or that air quality is impacting the health of local residents – the result in part of some very strange and short-sighted choices by the Planning Department on where to locate new residential developments. Inexplicably, our council continues to have a very ambivalent attitude to what should rightly be viewed as a key enabler of our economic prosperity.
‘The reality is, the healthy human desire to travel and see the world will not and should not be legislated away by those with a dystopian vision of the future.’
The reality is, the healthy human desire to travel and see the world will not and should not be legislated away by those with a dystopian vision of the future. The technical challenges to realising a cleaner way to fly are immense, but they are not uniquely Liverpool’s burden and no other city would so blindly hobble itself in restriction.
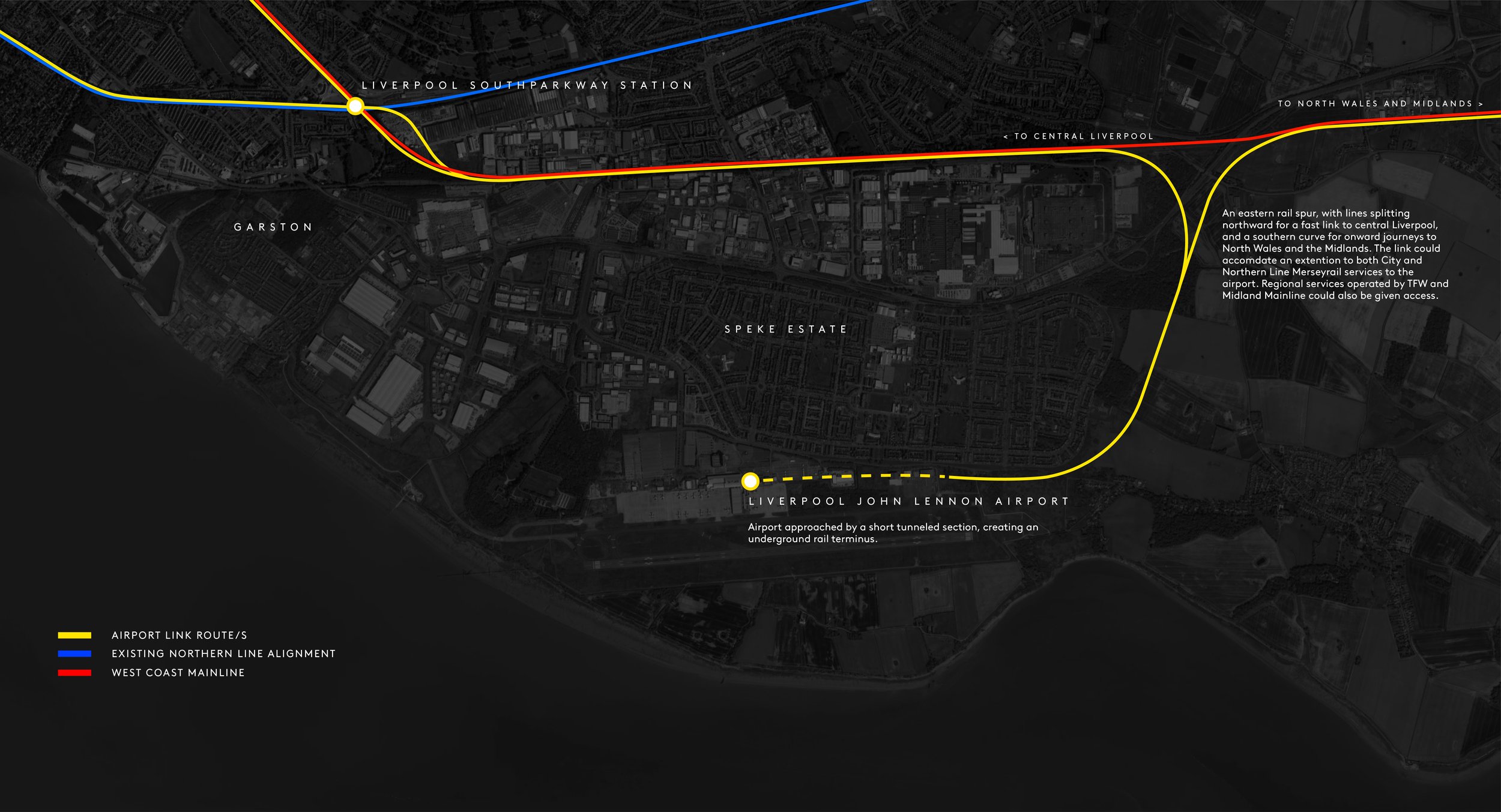
Michael McDonough grew up next to Liverpool John Lennon Airport and has seen its infrastructure grow from “a small, bland, industrial shed of a terminal into something more befitting,” and at some point in the future he believes it will need to expand. Michael argues that better public transport provision should be a priority with an extension of the Northern line or a tram connection mooted as alternatives. In these designs, Michael has proposed a train line that tracks underground for the final few hundred meters to arrive directly at a much expanded terminal. The capacity of the current structure is around 7 million, so if JLA can hold onto its post-Covid gains and continue to build upon them, discussions about what comes next will be inevitable. “The myopic few who claim the northwest already has a large airport and doesn’t need another, are shutting their eyes on the obvious.,” says Michael. “Demand for flying will continue to rise and the north can easily sustain a larger Liverpool John Lennon Airport at Speke.”
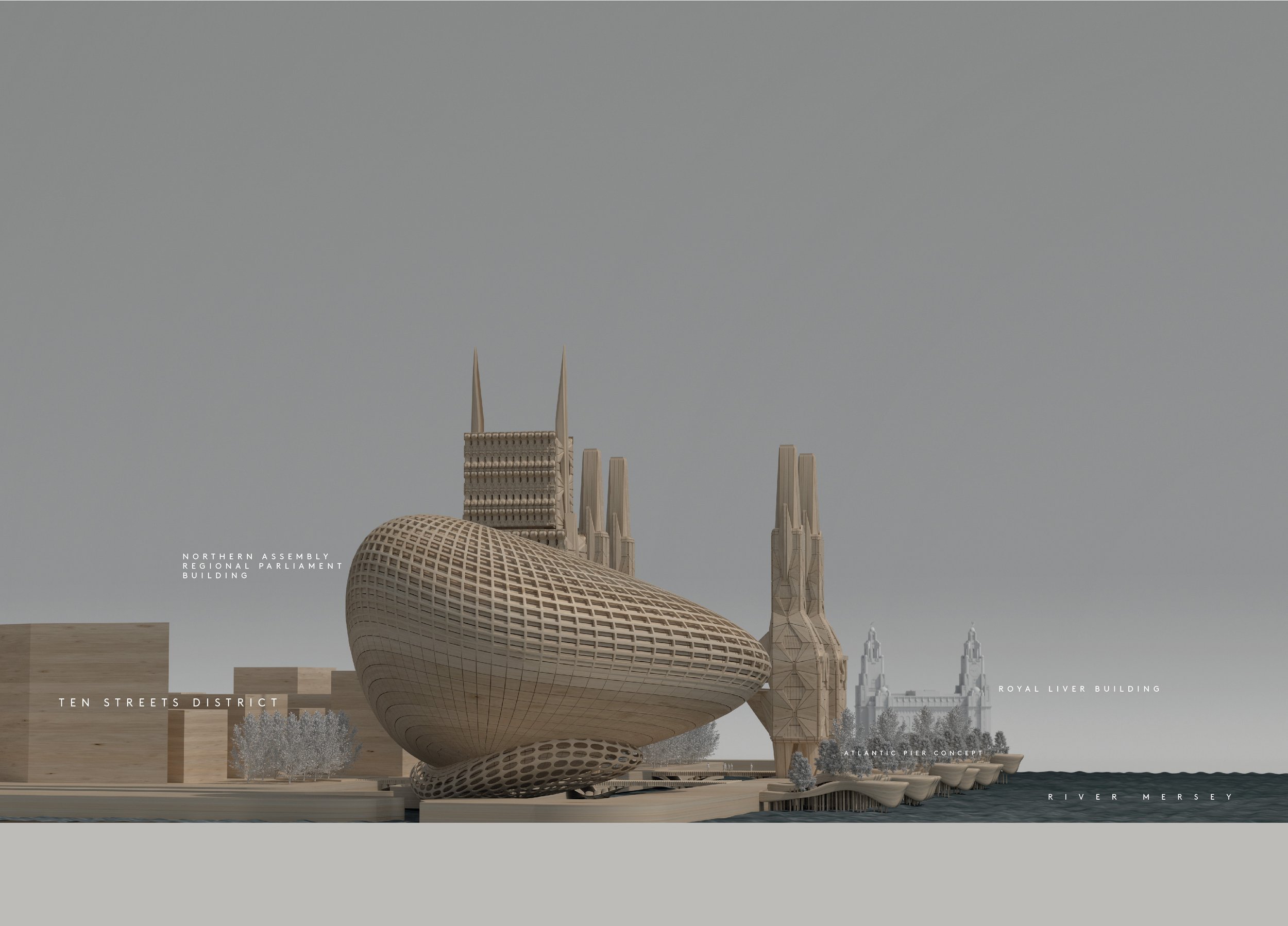
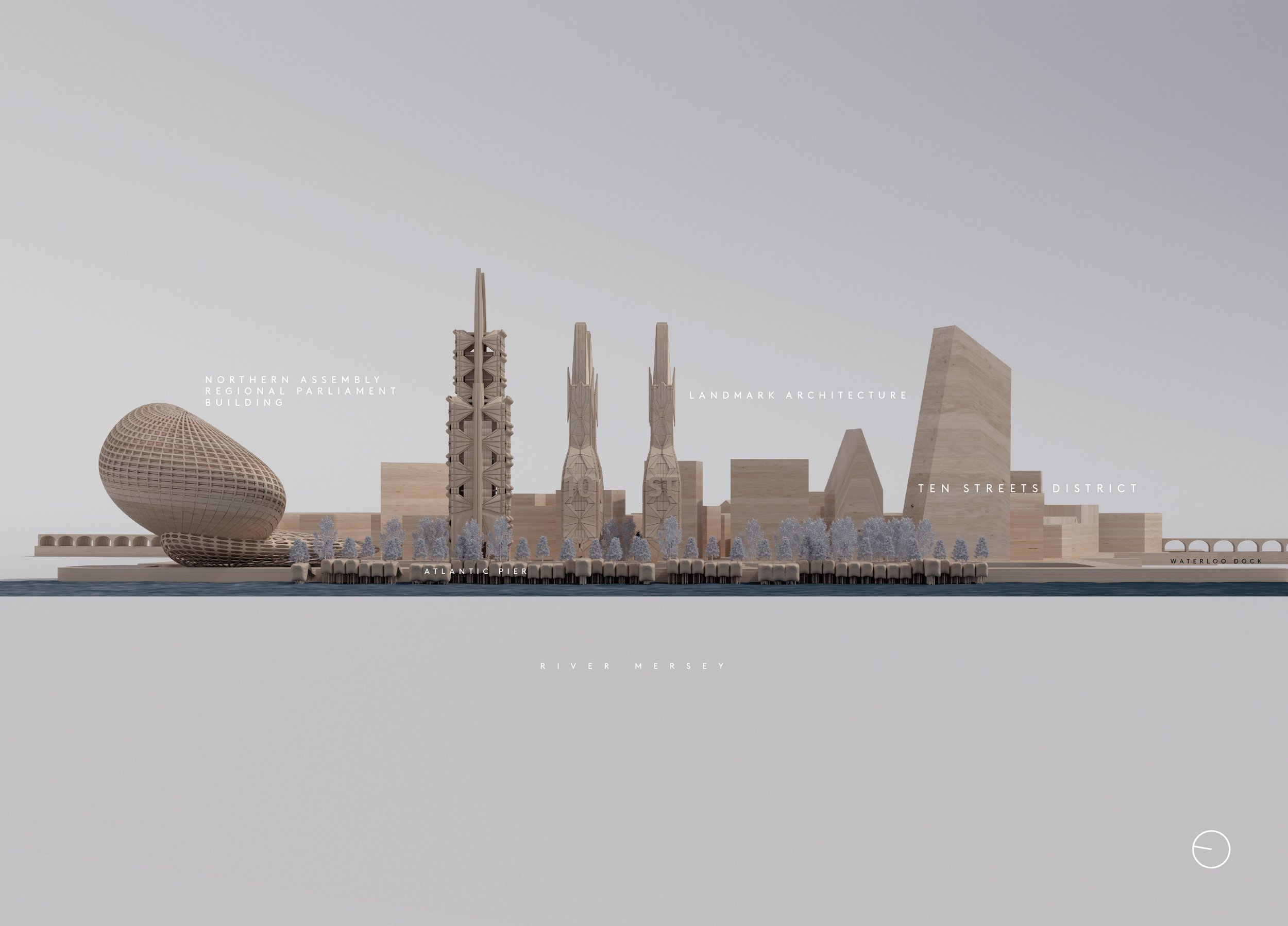
Northern Assembly
Given the shenanigans at Liverpool City Council in recent years, it might seem strange to suggest our city as the seat of political governance for the whole of the north. But a Labour government is a distinct possibility come 2025 and they’ve often flirted with the idea of greater regional devolution and a northern assembly to govern our unruly mob. Manchester is the usual default option, of course, but at Liverpolitan we can’t be having that. Perhaps only Newcastle can offer the grandeur of our riverside estuary setting here on the Mersey. Wouldn’t it be wonderful if Liverpool took inspiration from its darkest days to become a paragon of democratic values? To take accountability and citizen engagement as its governing principle, to put behind it the days of boss politics and party before city, and instead show the world how local government is done when at its best.
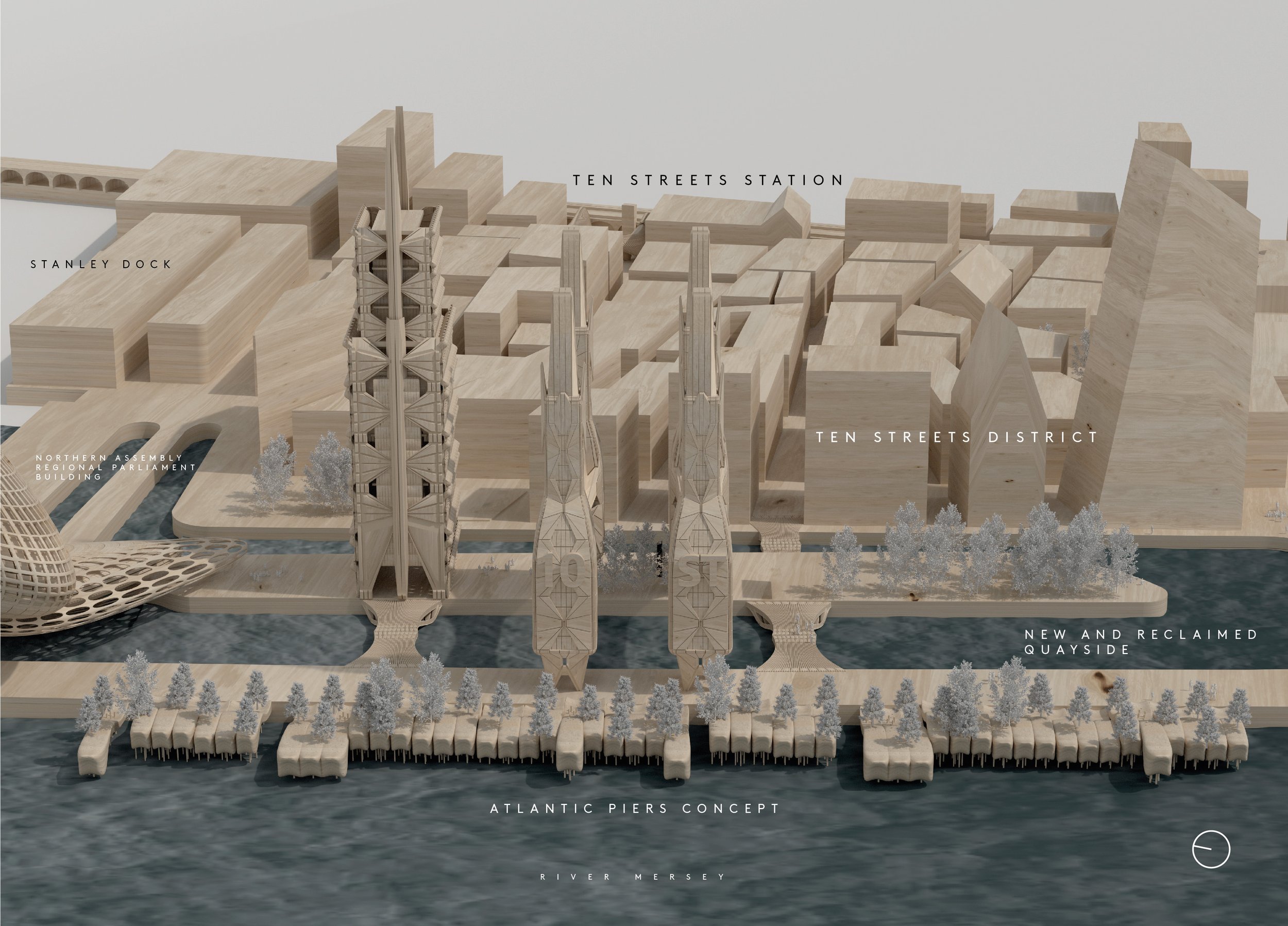
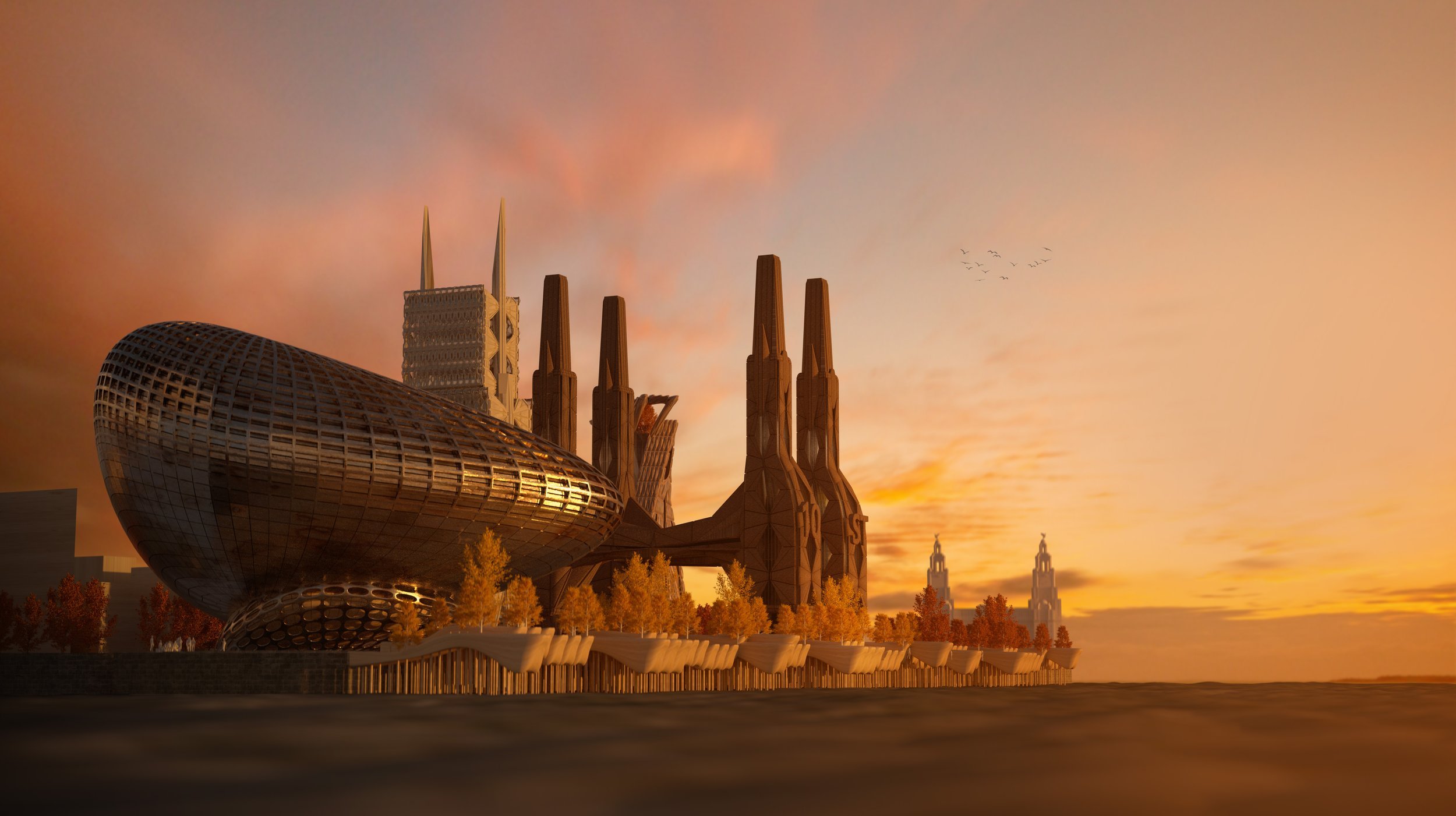
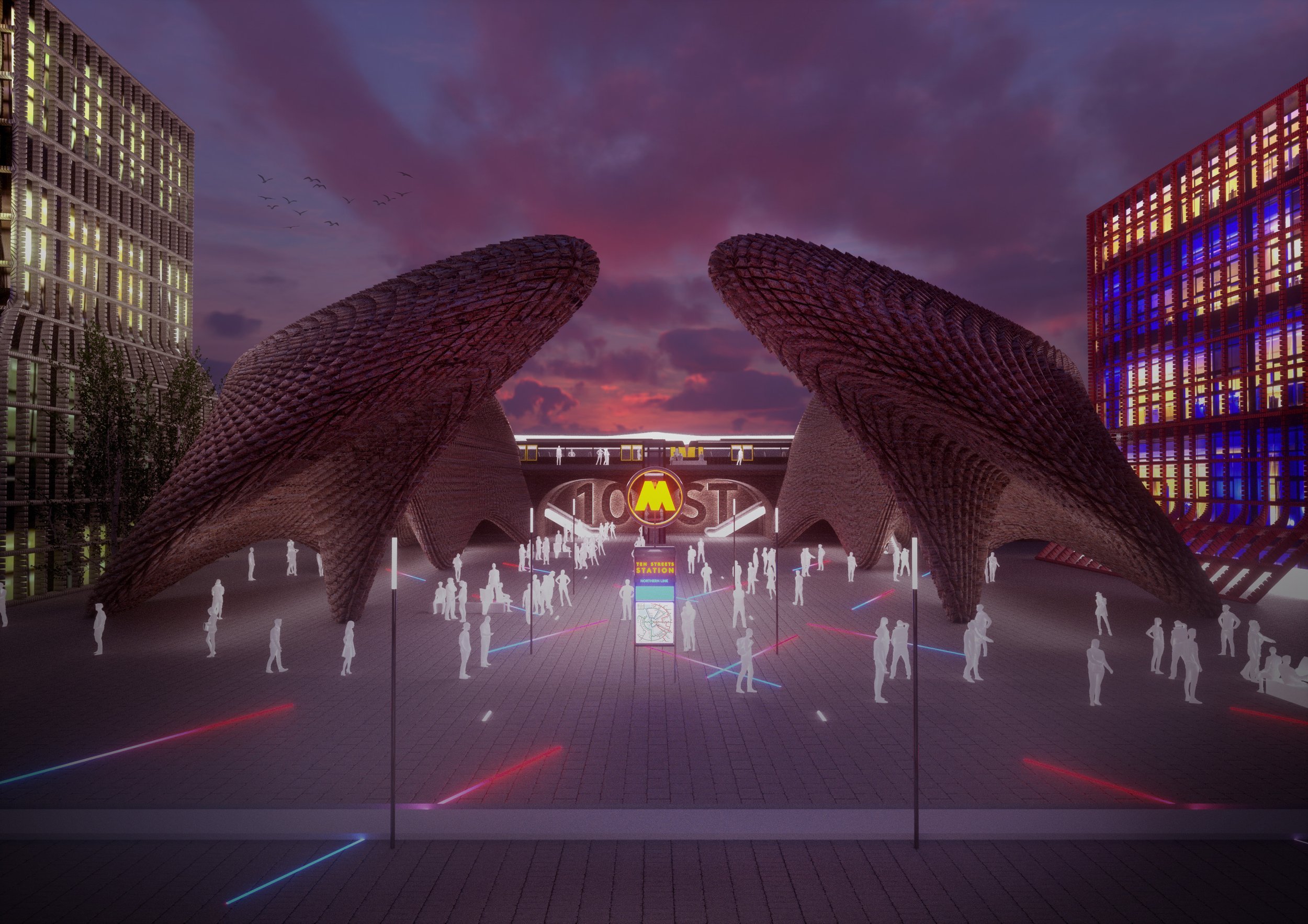
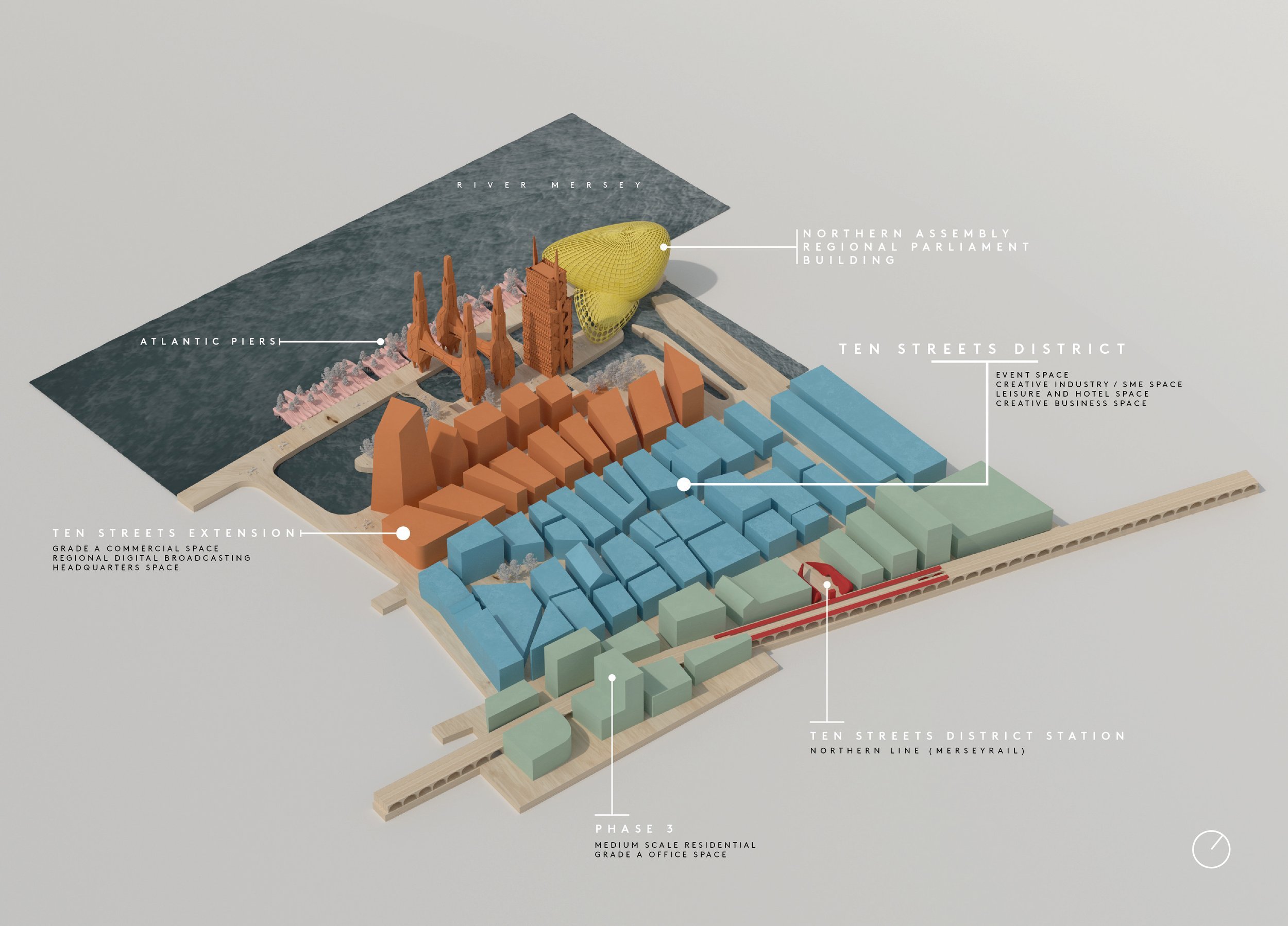
McDonough’s design of a new Assembly district is based on a wholly different concept to Peel’s current underwhelming plans for Liverpool’s central docks – albeit quite capable of incorporating a sizeable, new park. The site encompasses a parliament building, ancillary office space, a new cultural centre with notes of modern gothic and an extension of a revitalised mixed-use Ten Streets area including substantial residential to repopulate the area and give it life. In these days when the potential for terrorist attacks is sadly a design factor, Michael believes the location’s riverside setting has unique advantages, making it defensible for security services. Addressing concerns about the loss of ‘blue space’ at Waterloo Dock, he has increased the provision of waterways by reclaiming some of the infilled land, and bridging buildings across it. This Michael explains is “meant as both a symbolic and practical gesture of compromise in a city often at loggerheads with itself on how to reach for the stars architecturally without compromising existing heritage elements.”
Naturally, this substantial expansion of our city centre, requires transport infrastructure, which Michael has designed in with a new station at Vauxhall on the Northern line. Such investments in transport become more viable as we add additional all-year-round uses instead of just relying on the footfall that the new Bramley Moore stadium will provide.
‘Wouldn’t it be wonderful if Liverpool took inspiration from its darkest days to become a paragon of democratic values? To put behind it the days of boss politics and party before city, and instead show the world how local government is done at its best.’
For a fuller exploration of this concept, read Michael McDonough’s Liverpolitan feature, Welcome to the Assembly District.
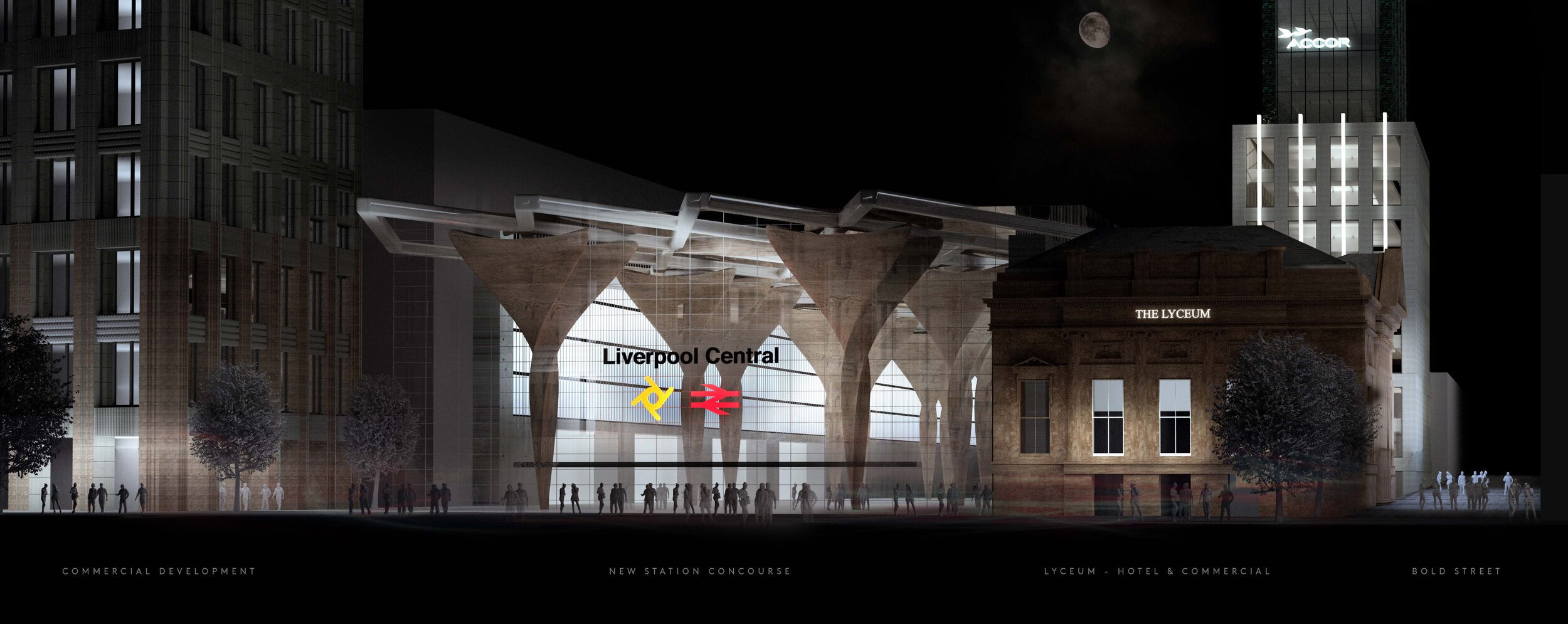
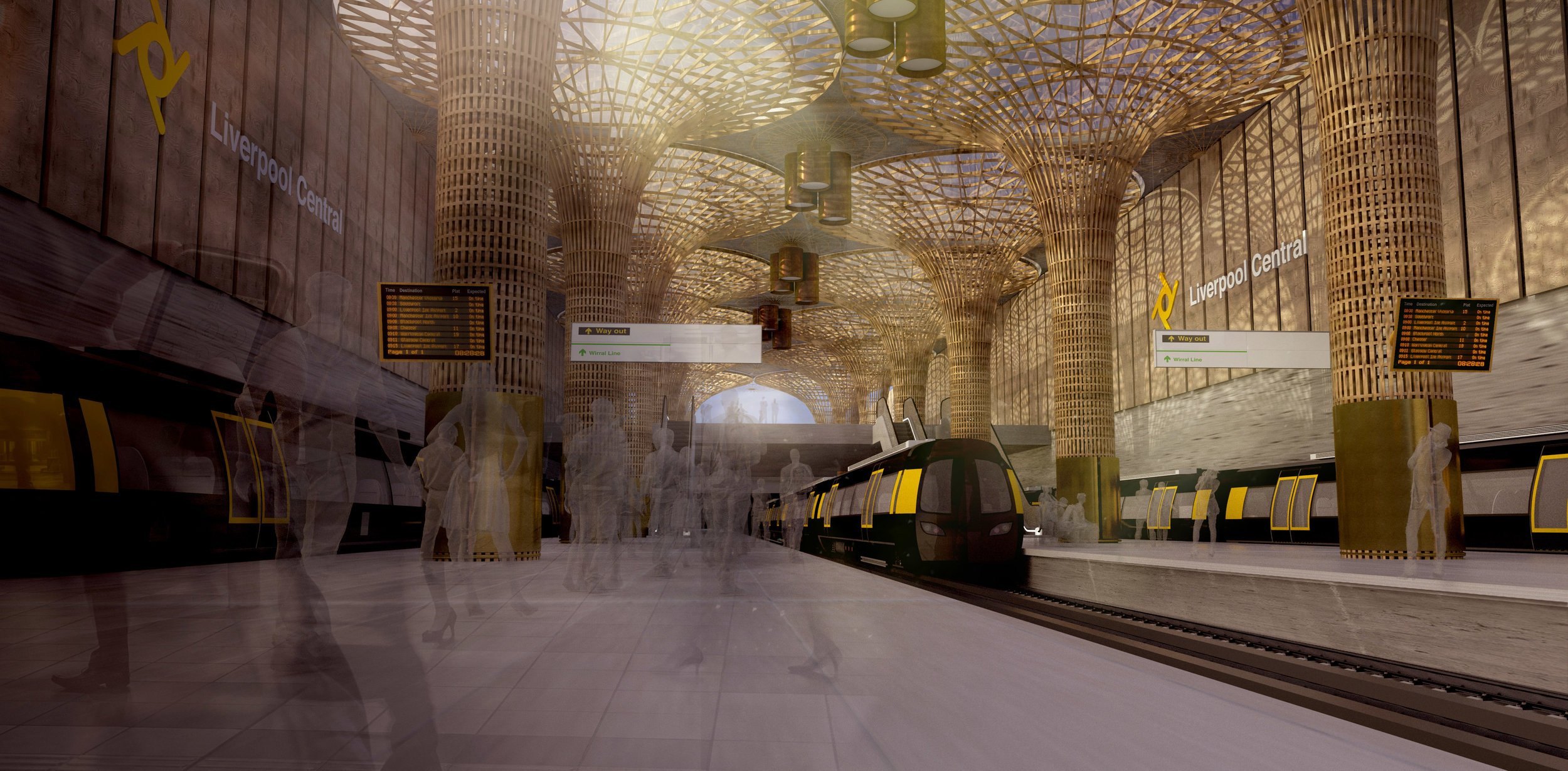
Liverpool Central Station
The redevelopment of Liverpool Central Station has long been on Merseytravel’s wish list and it’s not hard to understand why. Boasting the highest passenger numbers of any underground station in the UK outside of London, Liverpool Central is, despite recent minor refurbishment, “a dark, dated and cramped station prone to over-crowding,” according to Michael. Its current single island platform structure and track layout on the Northern Line section also places restrictions on train capacity. A full scale expansion of the station, which the Liverpool Combined Authority are pushing central government for, would allow more trains to run through services linking up the Northern and City lines via a re-used Wapping Tunnel. This would in turn free up capacity at Lime Street Station enabling it to focus on its role as an intercity and regional transport hub.
A few years ago there were grand plans to convert the old Lewis’ department store which sits next to Central Station into a new shopping centre accommodating new residential blocks. A side benefit of the scheme was the use of Lewis’ ground floor to open up a new, additional entrance to the station itself. However, the proposed scheme, which ultimately came to nothing, left intact the tired, almost prefab current station entrance – “a pale shadow of what was once a magnificent Victorian railway terminal,” says Michael.
McDonough believes that when the time comes to rebuild this thing, we should “go all out and design a station that lets in the light.” These visuals imagine a doubling in the size of the station envelope, with an additional platform, and the complete removal and replacement of the shopping arcade with a dedicated railway concourse at the street level front end. The plan would allow the floor above the underground platforms to be removed allowing sunlight to reach down to create a much more welcoming environment. Reinforced as a major local transport hub for the city, and with the poorly performing shopping centre now gone, Michael believes the wider site offers potential to “accommodate new office and residential accommodation at impressive scale.”
‘The proposed scheme, which ultimately came to nothing, left intact the tired, almost prefab current station entrance – a pale shadow of what was once a magnificent Victorian railway terminal.’
New Brighton Pier and Observation Tower
The advent of foreign travel certainly did for many of Britain’s seaside resorts. Still, nostalgia aside, glancing through old photographs of New Brighton does makes the heart bleed for what was lost. It’s hard to think of a more striking example of the region’s self-destructive attitude towards its built environment than the loss of the old ballroom and tower, fire or no fire. Not to mention its pier, pleasure grounds and lido. Daniel Davies of Rockpoint Leisure has been doing his bit in recent years to bring a bit of hip to Victoria Street and the Championship Adventure Golf course is well worth a visit too. In fact, there are tentative signs that Wirral Council are starting to understand what they have, even if the area has been stripped of many of its key attractions. Liverpool’s Left Bank can and should be a treasured beauty spot, a place for families to enjoy and a haven for the avante garde and edgy. Now is the time to think bigger.
Michael hasn’t yet worked on a full plan for New Brighton but bringing back some kind of landmark beacon with a viewing deck, visible from the other side of the Mersey and prominent to the passing cruise ships feels like it should be part of the picture. Back in the early 2000s, sculptor Tom Murphy proposed a 150-foot statue of the Roman god, Neptune, to sit in the waters at the mouth of our mighty river – Liverpool’s equivalent of the Statue of Liberty or the Colossus of Rhodes. Oh, how we’d like to have seen that! Or if money was no object, two of them either side of the river standing proud like the Argonaths of Lord of the Rings. In the meantime, Michael McDonough took a stab at a slightly less monumentalist beacon a few years ago.
‘Back in the early 2000s, sculptor Tom Murphy proposed a 150-foot statue of the Roman god, Neptune, to sit in the waters at the mouth of our mighty river – Liverpool’s equivalent of the Statue of Liberty or the Colossus of Rhodes.’
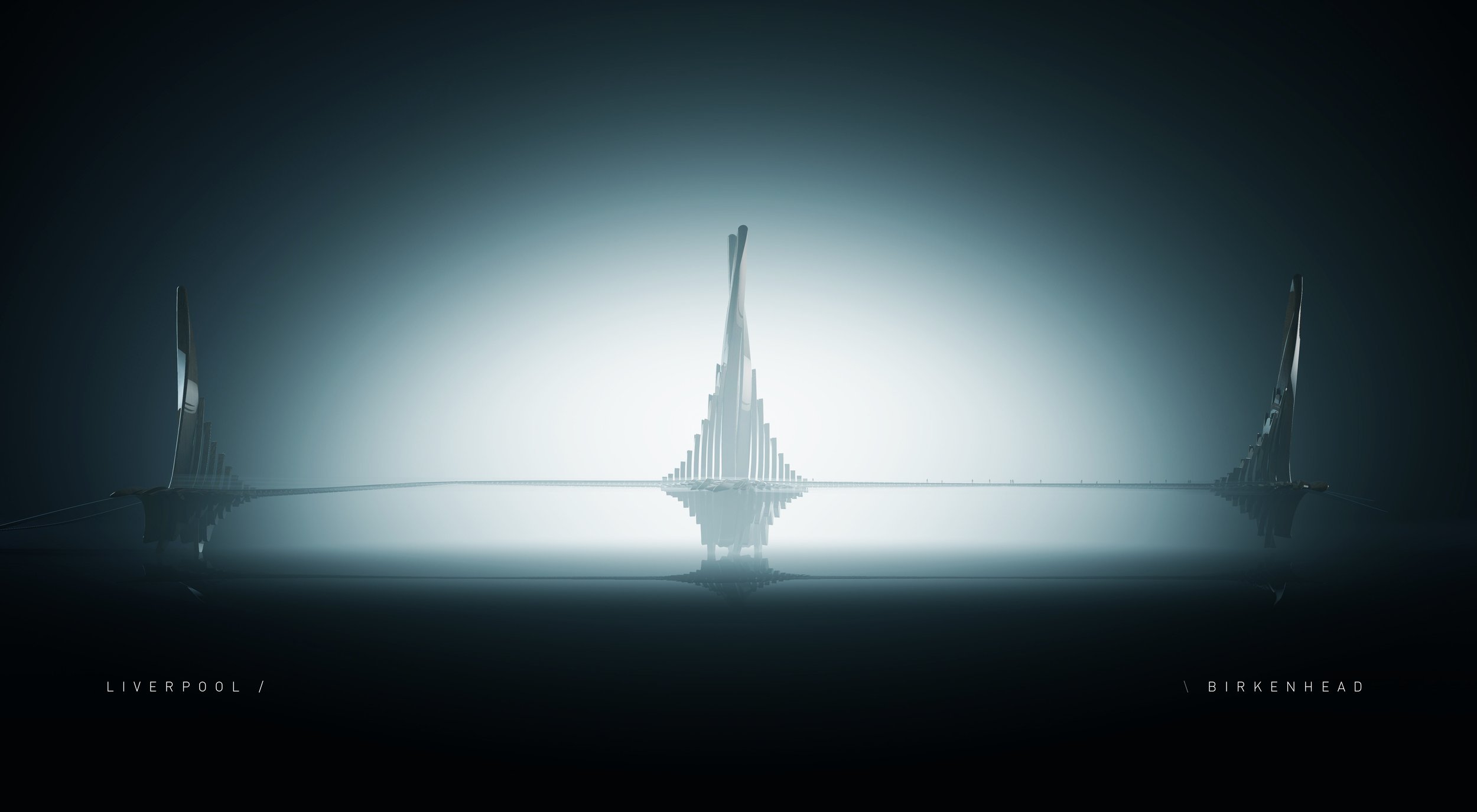
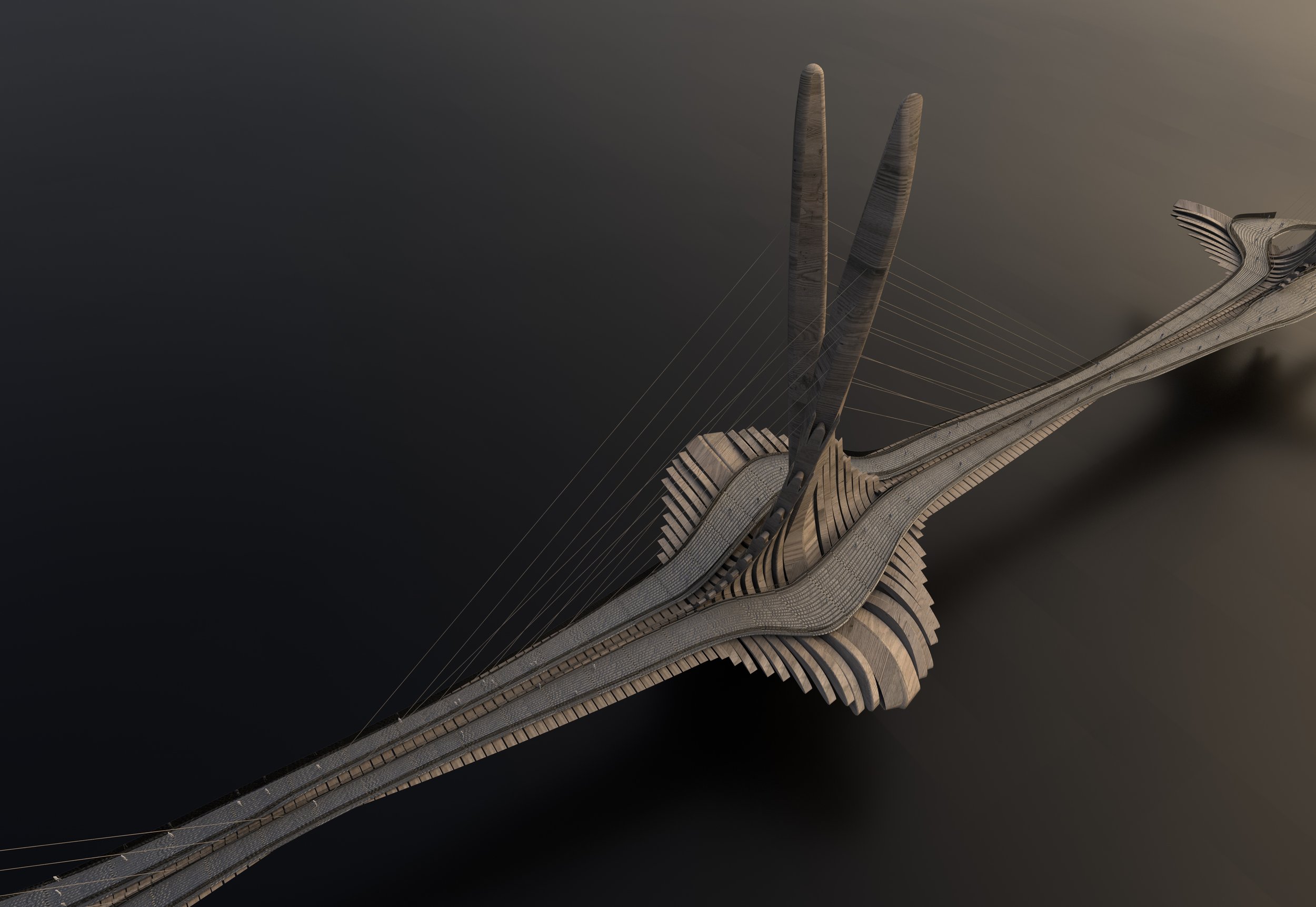
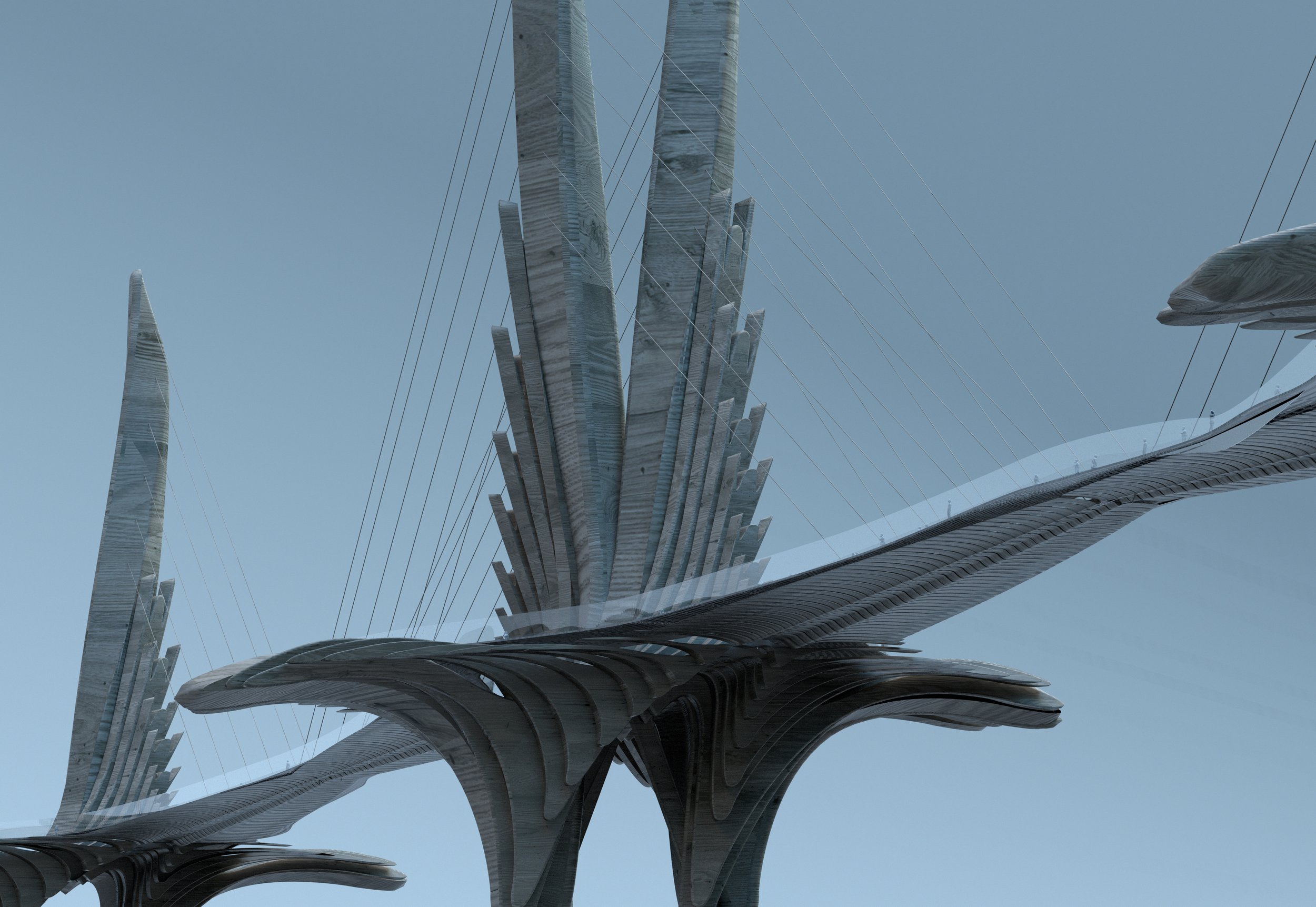
The Liverpool ‘Angel’ Bridge
Unashamedly a flight of fancy and almost certainly the most outlandish of McDonough’s ideas, the concept of a bridge linking Liverpool and Birkenhead delivers an element of San Francisco’s Golden Gate magic and then tries to one-up it. There’s something slightly Game of Thrones about this design, which Michael says he wasn’t consciously thinking about at the time. “It’s intended as statement architecture,” says McDonough, “A big ‘Here I am’ to the world that would forever add a new image to the iconography by which Liverpool is known.” The idea behind it is to unlock the two sides of the Mersey as one urban centre, transforming Birkenhead’s prospects for the better. It would, of course, be ludicrously expensive and so is likely to remain one for the mind’s eye. “Building this kind of structure would take serious doses of civic ambition and that’s the kind of vision we don’t often see in these parts,” said Michael.
For those worrying whether the bridge would undermine the Mersey tunnels, it has been designed as pedestrian-only, although it could be adapted to accommodate light rail or electric tram-buses. In terms of location, on the Liverpool side, Michael imagines it would sit between the Albert Dock and the Museum of Liverpool, while over at Birkenhead, the bridge would land at Woodside, right next to his alternate proposed site for an Opera House North.
“It’s intended as statement architecture”, says McDonough, “A big ‘Here I am’ to the world that would forever add a new image to the iconography by which Liverpool is known.”
…and finally.
Project vision and designs by Michael McDonough. Article by Paul Bryan.
Paul Bryan is the Editor and Co-Founder of Liverpolitan. He is also a freelance content writer, script editor, communications strategist and creative coach.
Michael McDonough is the Art Director and Co-Founder of Liverpolitan. He is also a lead creative specialising in 3D and animation, film and conceptual spatial design.
Share this article
What do you think? Let us know.
Write a letter for our Short Reads section, join the debate via Twitter or Facebook or just drop us a line at team@liverpolitan.co.uk
HS2 - A Liverpool coup?
The Department for Transport has released the ‘Integrated Rail Plan for the North and Midlands’ to much wailing and gnashing of teeth anywhere north of Birmingham. But is it really as bad as all that? What exactly does it mean for the future of the Liverpool City Region and its rail connectivity?
Michael McDonough & Paul Bryan
The Department for Transport has released the ‘Integrated Rail Plan for the North and Midlands’ to much wailing and gnashing of teeth anywhere north of Birmingham. But is it really as bad as all that? What exactly does it mean for the future of the Liverpool City Region and its rail connectivity?
Depending where you live, HS2 (or High Speed 2) has been seen either as a god-send for levelling up or a blight on pristine countryside. It’s been controversial from the start. Some of that has to do with the cost - after all you can buy quite a lot for the, by some estimates £100bn+ price tag. Some of it has to do with a sense of entitlement or environmental catastrophism in the home counties from the Not In My Back Yard brigade. But mostly, it’s the long-running sore of unequal investment, as northerners watch on jealously as one prestige project after another has been signed off around London. ‘When is it our turn?’, we asked and it seemed HS2 and HS3, subsequently christened Northern Powerhouse Rail, was the answer. Of course, Labour’s northern strongholds have long been suspicious, ever watchful for that knife in the back, and who can blame them? Rumours of nips and tucks to the ambitions of northern travellers have circulated for years and now those rumours have been put out of their misery. The eastern leg to Leeds is no more, Manchester is not getting it’s gold-plated underground station, Bradford is off the map and Newcastle, well they were never on it in the first place. But what about Liverpool?
‘The North’ is, and perhaps always was, a convenient ‘catch-all’ phrase used to hide the oh-so-obvious regeneration focus on Manchester.’
Watching the whole HS2 debacle from Liverpool has been something of a frustrating process. From the outset, our leaders have done their level-best impression of an ostrich with it’s head somewhere where the sun doesn’t shine. They never seemed to understand the existential threat that HS2 posed to the city in its ‘Manchester-friendly’ form. Ah, Manchester, that northern capital (self-appointed), who doesn’t dream of being relegated to commuter-town status to serve that inflated mill-town? At Liverpolitan, that’s long been our suspicion, since before we were a twinkle in our self-published eye(s). ‘The North’, is and perhaps always was a convenient ‘catch-all’ phrase used to hide the oh-so-obvious regeneration focus on Manchester and the lack of focus on other places like Liverpool, Bradford and Newcastle. The logic of agglomeration means all roads point east along the M62. Why don’t they just admit it instead of all this secret code stuff?
Which brings us back to the Integrated Rail Plan for the North and Midlands. If it’s true that ‘The North’ is something of a deception to hide the fact that its cities have competing interests, then maybe we should take off the northern hair shirt and look with fresh eyes at the government’s new plan. Forget about the others, what does it mean for Liverpool?
Manchester-centric
Before we tuck too far into that, it’s most probably worth a quick history lesson. The HS2 project was first launched in 2009 by the Labour government and then picked up a year later by the newly elected Conservative-Liberal Democrat Coalition administration. They quickly began a consultation on a route from London to Birmingham, with a Y-shaped section to Manchester and Leeds. High speed rail was to become one of the centre pieces of then Chancellor George Osbourne’s ‘vision’ for an all-inclusive ‘Northern Powerhouse’ (singular, not plural) viewed through the skewed lens of his Tatton, Cheshire constituency.
The resulting report and general direction of travel made it immediately clear that this mammoth piece of railway infrastructure was going to serve up yet another Manchester-centric political indulgence. The scales would be tipped conclusively in favour of ‘regional capitals’ such as Manchester and Leeds, relegating cities such as Liverpool and Sheffield to more tertiary positions. Liverpool’s obvious absence from visuals, media coverage and general debate around the HS2 project only seemed to re-enforce this essentially political idea. For some, it may have entrenched notions of ‘managed decline’ by an uncaring Conservative government but our Liverpool leaders didn’t seem to notice. Look trains! Trains good…
At the time, there were numerous debates and disputes around the data on rail capacity, BCR (benefits-cost ratio) and route alignments, all used to justify a heavy public investment on the Manchester, Birmingham and Leeds sections of the line. Train-spotter types got all exercised about it. There seemed to be some logical perversion going on. Liverpool it was argued, didn’t need more trains to London because there wasn’t enough passenger demand, but Leeds did need more trains because, well, they needed to stimulate more demand from the current low levels. Say what? It was like one of those National Lottery games where the outcome was already determined and you only had the illusion of choice. The data was made to fit the argument as far as the Liverpool City Region was concerned. Led by Transport Minister Lord Andrew Adonis, the plan for HS2 would leave Liverpool staring down the barrel of a future in which the struggle to stay economically competitive just got a little harder. The dice, it seemed, were stacked.
From the beginning Liverpool’s politicians didn’t seem on the ball. Even ones with a bit of clout weren’t really arguing Liverpool’s case. Maria Eagle (former Shadow Transport Minister) and Louise Ellman (Transport Select Committee) were strangely absent from the debate despite holding roles that would have helped give Liverpool a voice. It was only after the establishment of 20 Miles More, a campaigning lobby group which made the case for better Liverpool HS2 connections, that the city region’s leaders finally started to understand the peril and by then it was very much an uphill struggle. Our politicians had like Emperor Nero fiddled while Rome burned (according to legend).
Prioritising Planes
Meanwhile, to the east our friends in Greater Manchester had hit the jackpot, although it must be said, that forward-thinking and a pragmatic attitude to working with Conservative governments had certainly played their role. The HS2 alignment was to track away from Liverpool with its 1.6m inhabitants to serve a dedicated Manchester Airport station (and its Cheshire hinterlands) on the main trunk line. This gold plated promise, which would punishingly add to journey times between Liverpool and London came courtesy of a vague commitment to make a local ‘contribution’ to costs and a Chancellor whose own constituency sits perhaps coincidentally on the south western fringe of the city. Naturally, Manchester was also awarded with a further £7bn tunnel bored all the way to the city centre to meet a new station alongside Manchester Piccadilly.
In short, from the start HS2 pushed Liverpool to the periphery. The city region would be served by a slow lane connection using old tracks and with no promise of additional capacity. While Manchester and Leeds were drawing up plans for regenerated business quarters and glamorous city-pads off the back of huge station investments, some evidence pointed to the project causing a net loss in GVA (Gross Value Added) for the Liverpool City Region. No investment, no seat at the table and notably, no meaningful support from ‘The North’ to help Liverpool to benefit. That’s northern solidarity in action. Politician, Andy Burnham likes to speak for ‘the North’ but invariably only one city seems to benefit from his political manoeuvring.
It begs the question, whether Liverpool should de-couple itself from the pan-northern view that the government transport plans are a disaster. If the old plans weren’t so good for us, maybe the new plans are better? It is clear that Manchester and Leeds stood to gain the most from HS2 as previously defined. Now that the eastern leg of HS2 to Leeds has been entirely removed, maybe the focus of the benefits have moved a little closer to home.
Liverpool should take a more pragmatic view when assessing this change of direction and put the interests of our city first.
The Government’s New Plans
The first thing to say is that as far as the new Integrated Rail Plan is concerned, it’s a case of swings and roundabouts. Liverpool gains in some areas and loses in others. For HS2, things are looking much rosier, whereas the never fully committed to and still very much a paper project, Northern Powerhouse Rail has been downgraded. But one thing is clear. It is simply untrue to say, as Metro Mayor Steve Rotheram did, that the government have “chosen not to deliver anything at all.”
So let’s look at HS2. What the government is now proposing for Liverpool brings fast tracks much closer to the city. It’s better late than never ambitions to have a dedicated spur from the main route, while in no way fully delivered, have taken a major step forward. The argument that Liverpool is important enough to receive a better service appears after a long and bloody battle and against all the odds to have been won. Whereas before, Liverpool’s connection to the new rail network was situated some 40 miles away, just south of Crewe, under the latest proposal HS2 tracks will now run to Ditton Junction, approximately 11 miles distant and right on the outskirts of the city. This resolves one of the two main capacity constraints facing our part of the network and substantially increases the scope for an expansion of freight services - a key strategic goal for the growth of Liverpool’s port. It will achieve this by relieving the congested section of the West Coast Mainline (WCML) between Crewe and Weaver Junction (where the Liverpool branch connects) allowing many more freight paths towards the Midlands and the South. As an added bonus the revised route will also reduce journey times to London for passengers although by only a modest 2 minutes.
Those improvements will be achieved through a combination of new track linking Manchester to Warrington Bank Quay station and the use of the under-utlised Fiddler’s Ferry route which will be redeveloped and electrified (without a significant effect on existing passenger services).
Of course, what we all want is for new track to be laid all the way to central Liverpool serviced by a station with sufficient capacity to handle the additional services, as was discussed in Martin Sloman’s article, Lime Street or Bust? The options for Liverpool’s HS2 station. But we should point out in the interests of fairness, that a new station and new dedicated track is not and never has been on offer from the government; it’s just something we feel the city needs. To go those extra eleven miles and build a new station would, according to the report, require local funding. This is, of course, a ludicrous and hypocritical position for a national government to take (given the resources thrown at other cities) but there’s room for optimism. A future government may take a different view and once the engineers start to tuck into the final details and look at the numbers, the business case for raising ambitions further may become obvious. After all, the big argument for better Liverpool services has been won.
In the meantime, the rail plan proposes a solution to the second big capacity constraint facing Liverpool - the narrow throat that is the entrance to Lime Street Station. This acts as a significant break on the amount of trains that can come in and out of the station at any one time, producing that all too familiar Victorian-era crawl over the last mile. The report recognises this issue and proposes that development work should focus on altering Lime Street and its approaches. Intriguingly, it states that ‘Network Rail analysis also shows that Liverpool Lime Street station can be altered largely within the boundary of existing railway land to accommodate the proposed service levels resulting from HS2 and NPR.’ Further work, it says, is needed to confirm the precise scope of interventions. This clearly points towards a very significant re-modelling project for our station.
For too long Liverpool’s interests have been subsumed under a ‘Northwesternist’ agenda centred politically and economically on the needs of Manchester. It has been the failing of our local parties - all of them - Labour, Liberal, Conservatives and Greens to notice what has been going on.
If we move into the albeit not entirely reliable realms of speculation, the acceptance of the requirement to address Lime Street’s capacity constraints may open up a chink of light for the long overdue Edge Hill Spur, a project originally proposed in the 1970s. This would connect Liverpool Central station with the east of the city via the currently abandoned Wapping Tunnel to Edge Hill. If given the green light, local services could be moved out of Lime Street allowing it to concentrate on longer distance services. It would also precipitate the wholesale redevelopment of Central Station with all the benefits that would entail. We’re not saying it’s going to happen. Just that if you follow the logic of the report, it kind of makes sense.
Runcorn appears to be the big loser in this new plan, as it will no longer be on the HS2 map. But all is not lost for south Liverpool. A new station at Ditton Junction would serve the same market equally well and has to be an option as the detail of the plans are worked through. It is also not beyond the bounds of possibility that an expanded Lime Street could support a London-Runcorn service on the old WCML or provide a connection at Crewe.
One of the not really spoken about benefits of the new plan is that Liverpool’s new connections should now open at the same time as HS2 Phase 2B to Manchester. In an age when Liverpool must learn to compete with its northwest city brother in every field, this is an important win. Comparative journey time penalties to London will impact on our attractiveness to investors and although we do concede a 21-minute longer travel time, it would have been worse and in place for longer under the old plan. Marginal gains can add up.
As for Northern Powerhouse Rail, it’s hard to argue that we are now on anything but thinner gruel. Travel times to Manchester will not improve appreciably from the current levels offered to Victoria Station, and the Piccadilly route will be 6 minutes slower than was previously proposed. Trips between Liverpool-Leeds will also be slower, downgraded from 61 minutes to 73, although still significantly faster than the 106 minutes we experience today. Either way, as most people don’t like to commute for substantially more than one hour and tend to live in suburbs, not train stations, it’s never been truly convincing to believe that significant numbers would commute between the two cities of Liverpool and Leeds anyway. Nevertheless, in the cold light of day, NPR may not be what we dreamed of, but it’s still a significant step up from what we suffer in the present.
So despite the generally negative tone from media commentators and local politicians (who will be driven by their own political imperatives), the proposals carry with them some very sensible ideas. If implemented, the rail plan will mean the Liverpool City region benefits from:
New infrastructure for both HS2 and Northern Powerhouse Rail services
Improved capacity, journey times, frequencies and connectivity
Facilities will now open simultaneously with Phase 2B to Manchester
Andrew Morris of 20 Miles More told us, “The journalistic hype is quite different from the reality. My reading of the new plan is that, although imperfect, it’s a coup for Liverpool. Since the 20 Miles More campaign, the Liverpool City Region has raised its ambitions and engaged constructively with HM Government. The LCR has been unified and managed to navigate through the political quagmire the Department for Transport created when it threw in together all of the northern centres stakeholders. Yorkshire has lost out due to a lack of unity.”
It’s hard to square the comments of Andrew, who has been living and breathing train services for decades with those of Steve Rotherham, our Metro Mayor. He said, “Northern Powerhouse Rail had the chance to be transformational for our area and the wider north and important for the UK on the whole. But many voices including my own said they were going to deliver transformation on the cheap. Instead they’ve chosen not to deliver anything at all. We were promised Grand Designs, but we’ve had to settle for 60 Minute Make Over.”
The Manchester to Liverpool section of Northern Powerhouse Rail has been prioritised ahead of Manchester to Leeds. For Leeds and Bradford, that’s not good. But for Liverpool, well we should be OK with that. This is where we should have been from the beginning, because the Liverpool-Manchester axis has greater economic potential than the Manchester-Leeds one.
For too long Liverpool’s interests have been subsumed under a ‘Northwesternist’ agenda centred politically and economically on the needs of Manchester. It has been the failing of our local parties - all of them - Labour, Liberal, Conservatives and Greens to notice what has been going on. Instead, they were too busy picking their own small-time fights while competitor cities manoeuvred to advantage around us. Perhaps if our politicians adopted a more pragmatic approach to working with central government, whatever it’s political hue, we might not have needed campaigns like 20 Miles More in the first place.
As you wade through the interminable list of articles about the disaster that is the new Integrated Rail Plan, think on this… is it possible that most commentators are operating under a logical fallacy? That they have swallowed whole the idea that ‘The North’ is a single identity with common interests and that loss to one is loss to all? If we are being brutally honest, Liverpool may actually benefit competitively in a world where Leeds is a little more hobbled and where Manchester is not so dominant. It shouldn’t be a heresy to say so. Our brethren have been thinking exactly the same way behind closed doors for years. It’s time Liverpool joined the party.
Michael McDonough is the Art Director and a Co-Founder of Liverpolitan. He is also a lead creative specialising in 3D and animation, film and conceptual spatial design.
Paul Bryan is the Editor and Co-Founder of Liverpolitan. He is also a freelance content writer, script editor, communications strategist and creative coach.